2D shapes
Two-dimensional (2D) shapes are completely flat. They have two dimensions – length and width.
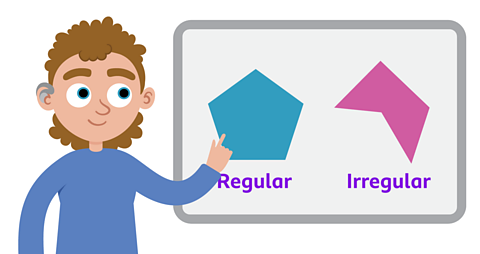
A polygon is a closed 2D shape with straight sides that meet at vertices. Polygons can be regular or irregular.
If all the straight sides of a shape are the same length and interior angles are the same size, then it is a regular polygon.
If the length of the sides are different and the angles are not the same size, then it is an irregular polygon.

Quiz: Identifying 2D shapes
Why not see how much you know about this topic already? Then complete the guide and see if you can beat your score.
Properties of 2D shapes
A property is a quality that a shape has.
Examples of shape properties are:
- number of sides
- number of vertices (corners)
- length of sides
- types of angles (acute, obtuse, right-angle)
- perpendicular and parallel lines
You can use a shape's properties to help identify and classify it.
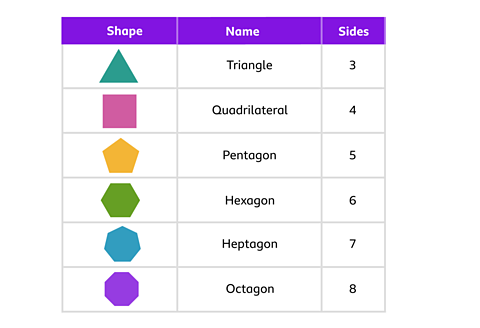
Polygons are named depending on the number of sides.
What is a polygon?
A polygon is a 2D shape with straight sides that meet at vertices.
Polygons have three or more sides. A circle is not a polygon because it doesn’t have straight sides.
Polygons can be regular or irregular.
A regular polygon has sides that are equal in length and equal angles.
These shapes are all regular polygons.

A regular triangle is called an equilateral triangle. A regular quadrilateral is called a square.
Irregular polygons are shapes that have sides and angles of different sizes.
You can always identify the polygon by how many sides it has. For example a pentagon is always a shape that has 5 sides.
Types of triangles
A triangle is a 2D shape with three sides.
There are four different triangles:
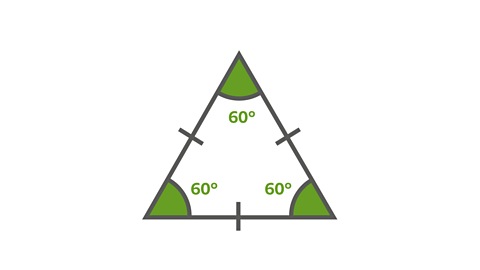
Image caption, Equilateral triangle
An equilateral triangle has 3 sides of equal length. The dashes on the lines show they are equal in length. All of the angles are also equal.
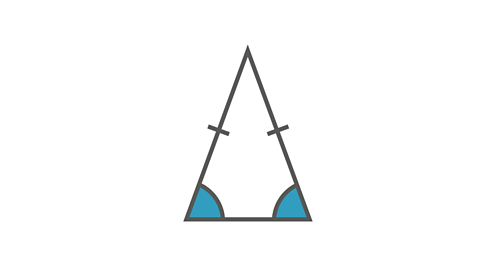
Image caption, Isosceles triangle
An isosceles triangle has 2 sides of equal length. The angles at the base of the equal sides are equal.
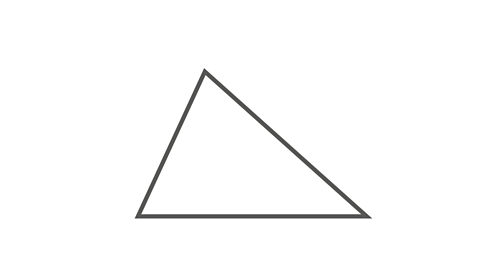
Image caption, Scalene triangle
A scalene triangle has 3 sides of different lengths and 3 unequal angles.
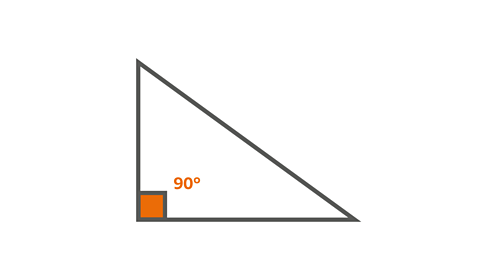
Image caption, Right-angled triangle
A right-angled triangle is a triangle that has a right angle.
1 of 4
Angles in a triangle
The angles inside a shape are called interior angles.
The interior angles in a triangle always add up to 180°.
You can use this facts to calculate missing angles in a triangle.
Take a look at this triangle. The angle labelled b is missing.

You know that one of the angles is 50°. The angle marked with a little square indicates that it is 90°.
You know that the interior angles of a triangle should add up to 180°. Therefore, you can subtract these values from 180° to find the missing angle.
180° - 90° - 50° = 40°
So angle b is 40°.
Types quadrilaterals
A quadrilateral is a 2D shape with four sides.
There are six special quadrilaterals with different properties.
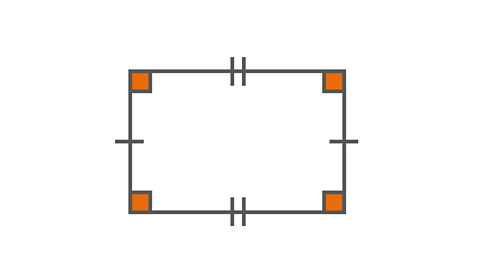
Image caption, Rectangle
A rectangle has two pairs of equal parallel sides. The interior angles are all right angles.
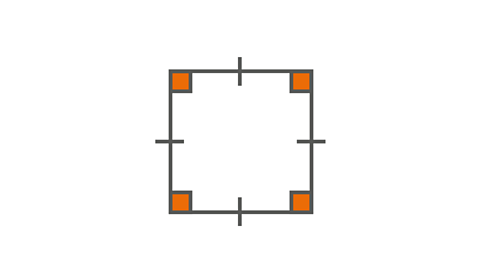
Image caption, Sqaure
A square is a special type of rectangle. It has four equal parallel sides and four angles that are right angles.
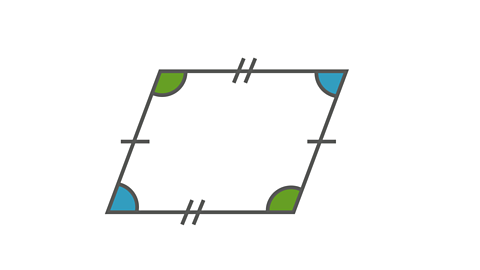
Image caption, Parallelogram
A parallelogram has 2 pairs of equal sides. The interior angles that are diagonally opposite each other are equal.
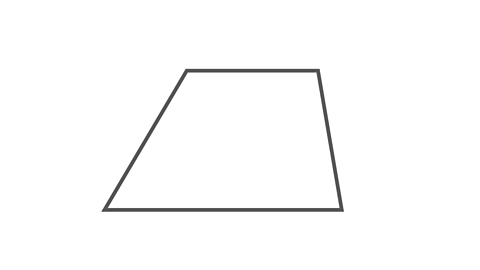
Image caption, Trapezium
A trapezium has one pair of parallel sides.
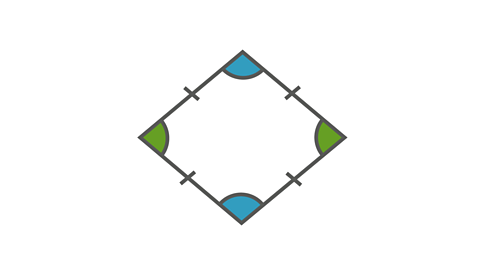
Image caption, Rhombus
A rhombus has four sides of equal length. It has two pairs of equal angles. The angles that are diagonally opposite each other are equal.
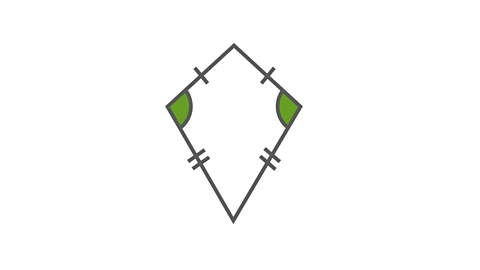
Image caption, Kite
A kite has two pairs of sides of equal length. It has one pair of equal angles.
1 of 6
Angles in a quadrilateral
The sum of the interior angles in a quadrilateral always add up to 360°.
Like with triangles, you can use this fact to find missing angles in a quadrilateral.
Take a look at this shape. Let's work out the missing angle labelled 'd'.
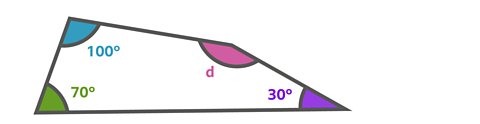
You know that all the angles in this quadrilateral should add up to 360°.
Three angles are labelled - 100°, 70° and 30°. To find the missing angle, you can subtract these values from 360°.
360° - 100° - 70° - 30° = 160°
Therefore, the angle 'd' is 160°.
Example 1
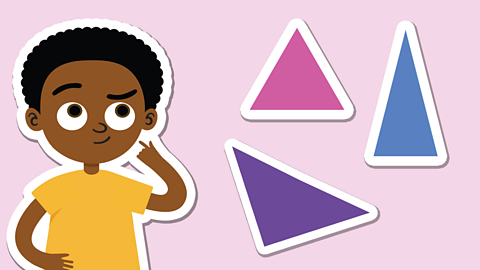
Kevin has drawn 3 polygons.
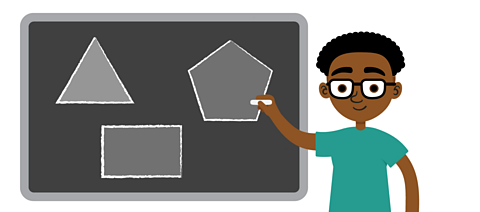
Kevin says that all the shapes are regular polygons because all the angles in each shape are the same. Is he correct?
✓ Kevin isn’t correct. A regular polygon has equal sides and equal angles. That means that the rectangle is not a regular polygon.
Even though a rectangle has four equal angles, it does not have sides that are all equal length.
Example 2
Two of the angles in this isosceles triangles are missing.
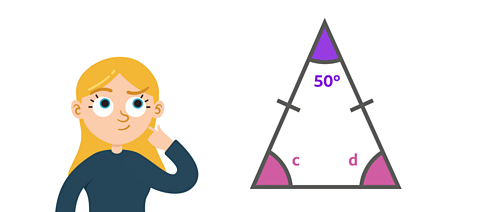
How would you find two missing angles on an isosceles triangle?
✓ Use your knowledge about isosceles triangles. An isosceles triangle has 2 sides of equal length. The angles at the base are equal.
You also know that the interior angles in a triangle always add up to 180°.
Find out what the total missing value is first:
180° - 50° = 130°
Angles c and d must now both equal 130°. Since we know these angles are both equal, you can find their value by halving 130°.
130° ÷ 2 = 65°
So c = 65° and d = 65°
More on 2d shapes
Find out more by working through a topic
- count2 of 10
- count3 of 10

- count4 of 10

- count5 of 10