Key points about one- and two-step linear equations

- Solving an equationA mathematical statement showing that two expressions are equal. The expressions are linked with the symbol =. means finding the value of an unknown variableA quantity that can take on a range of values, often represented by a letter, eg 𝑛, 𝑥, 𝑦, 𝑧, 𝑡 … etc. so that the equation is true.
- Equations are solved by using inverse operationThe opposite of a mathematical process. For example, the inverse of × 5 is ÷ 5. The inverse operation undoes the original process. .
- Equations such as 𝑥 – 5 = 12 need one step to solve. Equations such as 3𝑥 + 8 = 15 need two steps.
Make sure you are confident in calculating with negative numbers, which is a skill often needed to solve equations.
Check your understanding
Solving equations with one step
An equation is a mathematical statement showing that two expressionA mathematical sentence made up of one or more terms expressed either numerically or symbolically. are equal. It includes an equals (=) sign, and an unknown variableAn unknown value, usually represented by a letter such as 𝒙 or 𝒚., usually the letter 𝑥.
Solving an equation is the process of working out the value of 𝑥.
To solve an equation, inverse operationThe opposite of a mathematical process, eg, the inverse of × 5 is ÷ 5. The inverse operation undoes the original process. are performed on both sides until the value for 𝑥 is known.
The simplest equations have just one inverse operation to perform.
Follow the working out below
Exam style questions
- Solve 𝑤 – 8 = –2.
𝑤 = 6
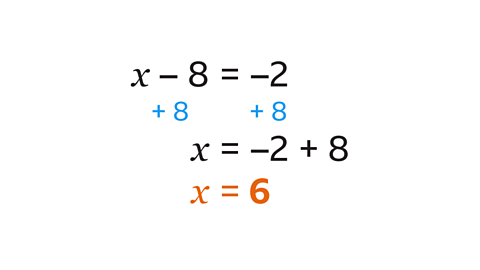
To solve the equation, do the inverse operation. The inverse of subtracting 8 is adding 8. Adding 8 to both sides gives the solution 𝑤 = 6.
- Solve 12𝑑 = 3.
𝑑 = \(\frac{1}{4}\)
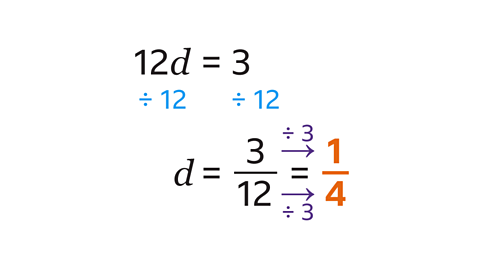
To solve the equation, do the inverse operation. The inverse of multiplying by 12 is dividing by 12. A fraction line can be used to show ‘divide by’. Simplify the fraction by dividing the numerator and denominator by 3.
Solving equations with more than one step
Sometimes equations require more than one step to solve them.
The process of solving an equation involves isolating the variableAn unknown value, usually represented by a letter such as 𝒙 or 𝒚. so that the letter terms are on one side of the equals sign, and the number terms are on the other.
To solve an equation, inverse operationThe opposite of a mathematical process, eg, the inverse of × 5 is ÷ 5. The inverse operation undoes the original process. are performed on both sides until the value for 𝑥 is known.
When solving an equation involves more than one step, the steps must be performed in the correct order.
The solution can be checked by subsittuteIn algebra, to replace a letter with a number. the answer into the original equation.
Follow the working out below
Exam style questions
- Solve 5𝑥 + 12 = 2.
𝑥 = –2
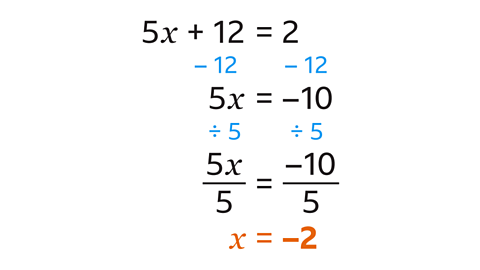
- Subtract 12 from both sides.
- Divide both sides by 5.
- The solution is 𝑥 = –2.
- Check the answer by substituting –2 in place of 𝑥 in the original equation:
5𝑥 – 2 + 12 = –10 + 12 = 2
- Solve 2𝑦 + 5𝑦 – 100 = 180.
𝑦 = 40
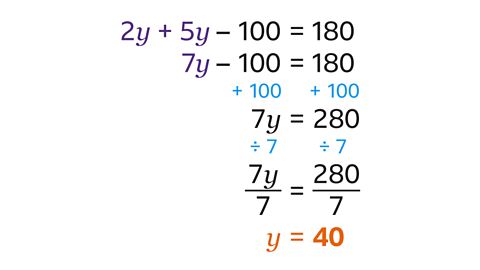
- Simplify the left-hand side by collecting the 𝑦 terms together.
- Add 100 to both sides.
- Divide both sides by 7.
- The solution is 𝑦 = 40.
- Check the answer by substituting 40 in place of 𝑦 in the original equation:
2 × 40 + 5 × 40 – 100
= 80 + 200 – 100
= 180, so the answer is correct.
Quiz – Solving one- and two-step equations
Practise what you have learned about solving one- and two-step equations with this quiz.
Now you have revised how to solve one- and two- step equations, why not take a look at formulae?
More on Algebra
Find out more by working through a topic
- count7 of 14

- count8 of 14
- count9 of 14
- count10 of 14
