What are nitrates?
Nitrogen gas makes up 78% of Earth’s atmosphere and is an essential element in amino acids and proteins.
However, plants and animals cannot use nitrogen gas directly.
Plants can only absorb nitrogen in the form of nitrateThe chemical absorbed from the soil by plants to produce their protein..
Minerals
Watch: Understanding plant minerals and euthrophication
Root hair cells, which are specially adapted, take in water and essential minerals from the soil, including:
nitrates for making amino acids and proteins
calcium for strengthening cell walls
magnesium for chlorophyll production
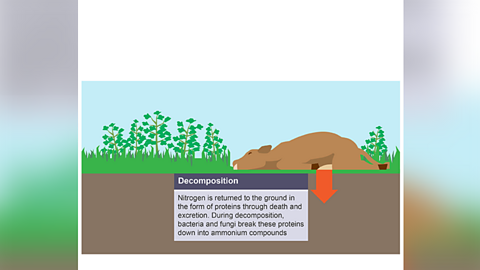
Image caption, Decomposition
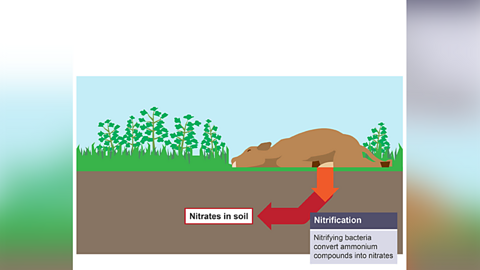
Image caption, Nitrification
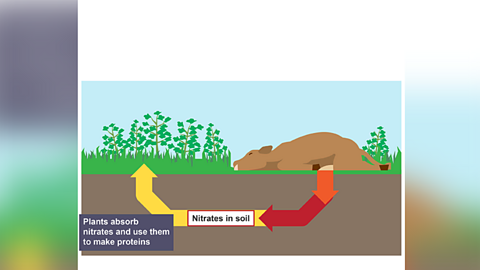
Image caption, Plant absorption
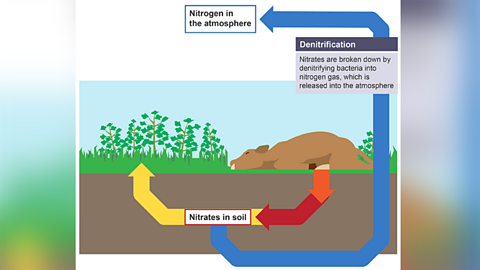
Image caption, Denitrification
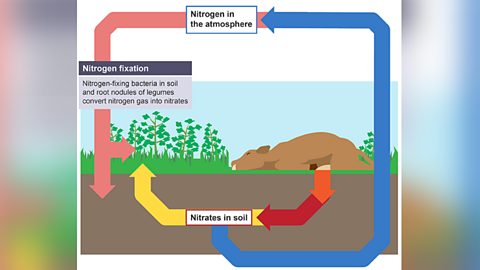
Image caption, Nitrogen fixation
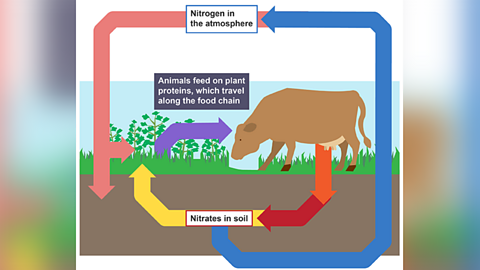
Image caption, Feeding
1 of 6
Root hair cells have a long extension that provides a large surface area for absorbing water and minerals.
Nitrates are absorbed by active transport, moving from a low concentration in the soil to a high concentration in the plant root, against the concentration gradient.
This process requires energy from aerobic respirationRespiration that requires oxygen., meaning it occurs only in the presence of oxygen.
What is the Nitrogen cycle?
Nitrogen is transferred between living organisms and their environment.
Bacteria carry out the following processes in the nitrogen cycle:
Nitrogen fixation
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria convert nitrogen gas into nitrates.
These bacteria can be found "free" in the soil or in nodules on the roots of plants like peas, beans, and clover.
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria need oxygen, as they are aerobic.
Decomposition
- Bacteria/fungi break down protein found in dead plants and animals, urine and faecesWaste matter from the bowels. into ammonia.
Nitrification
Ammonia is converted into nitrates by nitrifying bacteria.
Nitrifying bacteria needs oxygen as they are aerobic.
Denitrification
Nitrates are converted into nitrogen gas by denitrifying bacteria.
These bacteria thrive in waterlogged soil as they are anaerobicRespiration in the absence of oxygen. and do not need oxygen.
Denitrification reduces soil fertility and plant growth.
Ploughing soil and improving drainage reduces the number of denitrifying bacteria.
What are fertilisers used for?
Farmers use natural fertilisers (eg farmyard manure, slurry, compost) or artificial fertilisers to replace nutrients lost when crops are harvested.
Fertilisers mainly contain nitrates that help crops grow.
If nutrients are removed but not replaced the soil will eventually lose its ability to grow crops.

What is eutrophication?
Eutrophication is caused when sewage or fertilisers get leached (washed off soil by rain) into rivers and lakes.

Eutrophication process
- Increase nitrate levels
- Sewage disposal and fertiliser run-off increase nitrates level in rivers.
- Nitrates cause increased growth of aquatic plants and algae – known as an algal bloom.
- Plants die
- Algae and plants become overcrowded, shading each other and blocking light for photosynthesis, causing them to die.
- Decomposition
- Aerobic bacteria break down dead plants and algae.
- Oxygen Depletion
- Bacteria use up oxygen for respiration.
- Fish and other organisms die from a lack of oxygen.
Controlling the use of fertiliser and storing manure and slurry more securely can reduce eutrophication.
Test your knowledge
More on Biodiversity
Find out more by working through a topic
- count1 of 5

- count2 of 5

- count3 of 5
