Key points
Inequalities are used to describe the relationship between expressions that are not equal. They can be presented algebraically, in words, or on a number line.
The two sides in an equationA mathematical statement showing that two expressions are equal. The expressions are linked with the symbol = are equal. This is not the case in an inequality, as one side may be greater than (or less than) the other.
An inequality can have multiple solutions. When a single inequality is used there can be an infiniteUnlimited, unending. An infinite number of solutions means that they cannot be quantified. For example, there are an infinite number of integers that are more than 4 number of solutions. In some cases, the number of solutions can be finiteA fixed amount. There are a finite number of integers less than 10 and greater than 7. There are two such integers, 8 and 9. For example, when the unknown value is an integerIntegers are numbers with no fraction or decimal part. They can be positive, negative or zero. 42, 8, and 10000 are examples of integers. and between two given values.
Solutions to an inequality may be given as a simplified inequality, a finite list of values, a solution setOne way of listing the integer values that are correct for an equation or inequality. The values are written inside curly brackets, for example {4, 5} means that 4 and 5 are the integer solutions. or as an illustration on a number line.

Video
Watch the video to learn how Shahan, a video games developer, uses inequalities in his work and find out why inequalities are important when it comes to designing new video games.
Bobby: So, can you tell me about your work in game development?
Shahan: Yeah, definitely. So I’ve been doing a little bit of game design for a while but mainly what I do is game development. And that will consist of coding, lots of the backend nitty-gritty stuff.
Bobby: What type of games do you work on?
Shahan: So, I’ve done all sorts. I’ve done RPGs, a horror game called Incrementum and right now, I’m just finishing up on a little 2D side-scroller called Spirited.
Bobby: So, tell me a bit more about Spirited.
Shahan: Yeah, so in Spirited the idea is you play as a little ghost and to progress to the next level, you need to collect a number of gems.
Bobby: Hmm, to me, that sounds like an inequality. Can you give me a bit more explanation?
Shahan: Absolutely, so the idea is that if you collect and you have spirit gems that are greater than your minimum, then you progress.
Bobby: What about an inequality that is 'less than'?
Shahan: So, for 'less than', I’ve made a game called Full Stride. It’s a racing game, you have two players and whoever is the quickest out of the two players wins.
Bobby: Ah so, mathematically, to win, you need a time less than your opponent.
Shahan: Exactly.
Bobby: And what about the influences of the inequality that's 'greater than or equal to', or 'less than or equal to'?
Shahan: So, I’ve got an RPG game where you can go into villages and buy equipment in the same way that we would buy things in a shop. If you want a piece of equipment, you need to have greater than or equal to the number of coins that it costs.
Bobby: Inequalities sound really important to your work.
Shahan: Absolutely, they are completely vital. The great thing about inequalities is you can have lots of simple single inequalities and layer them up to build a really complex system of game.
Bobby: So, where else do you see maths in your work?
Shahan: Absolutely everywhere. I mean, just things like angles and coordinates come up when I’m designing a level and placing obstacles in different places. And so it’s really essential in everything when it comes down to coding.
Bobby: Thanks so much for sharing your insight into how inequalities, in fact maths as a whole, is really critical to game development.
Shahan: My pleasure.
Understanding and using inequality symbols
Inequality symbols are used when values are not equal.
The algebraic notationA series or system of written symbols used to represent numbers, amounts or elements in mathematics. used when writing inequalities is: ≠, <, ≤, > or ≥, where:
- ≠ means ‘not equal to’
- < means ‘less than’
- > means ‘greater than’
- ≤ means ‘less than or equal to’
- ≥ means ‘greater than or equal to’
Examples
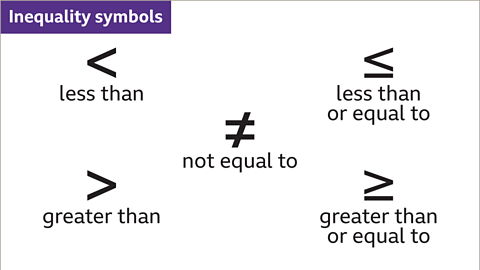
Image caption, The inequality symbols are used when values are not equal.
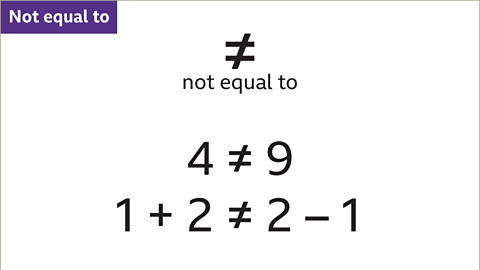
Image caption, When each side of the inequality are not equal the ‘not equal to’ symbol may be used. 4 is not equal to 9. The sum (1 + 2 = 3) is not equal to the difference (2 – 1 = 1). The ‘not equal to’ symbol does not order the values, it just states that they are not the same.
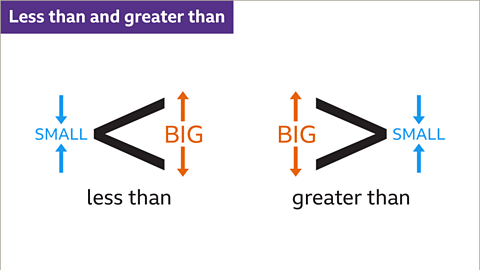
Image caption, The ‘less than’ and ‘greater than’ symbols give a comparison. The smaller end always points towards the lesser value. The bigger end opens out to the greater value.
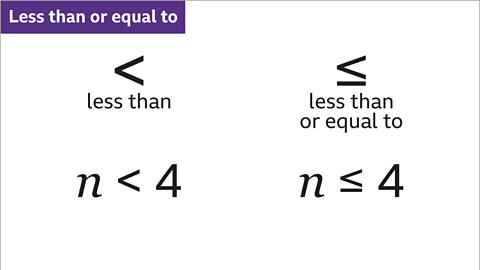
Image caption, 𝒏 < 4 means 𝒏 is less than 4. The value of 𝒏 is any number that is smaller than 4. This could be 3, 2, 1, 0, – 1, – 2 and so on for integers. The value of 𝒏 can also be a decimal or fraction, such as, 3۰9, 2۰15, and ¾ . The symbol ‘less than or equal to’ means that 𝒏 can also have the value that is given. In this example, 𝒏 could be 4 as well as any value less than 4. For both statements there are an infinite number of values that 𝒏 can take.
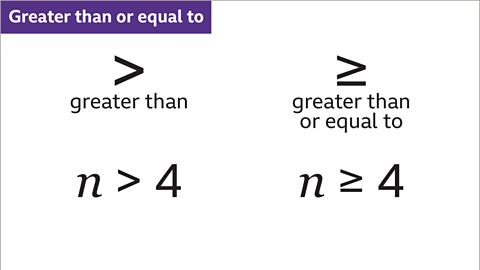
Image caption, 𝒏 > 4 means 𝒏 is greater than 4. The value of 𝒏 is any number that is bigger than 4. This could be 5, 6, 7, 8, and so on for integers. The value of 𝒏 can also be a decimal or fraction, such as 4۰1, 5¾, and 9۰02. The symbol greater than or equal to means that 𝒏 can also have the value that is given. In this example, 𝒏 could be 4 as well as any value greater than 4. For both statements there are an infinite number of values that 𝒏 can take.
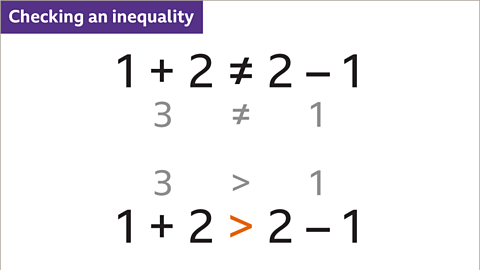
Image caption, The sum 1 + 2 is not equal to the difference 2 – 1. 3 is not equal to 1. Working out the answer to each expression checks whether the inequality statement is correct. The inequality can also be written as 1 + 2 > 2 – 1 because 3 > 1 (3 is greater than 1).

Image caption, The expression on each side of the inequality is worked out to check that the inequality is true. 3 – 7 = –4 and –4 is greater than 5. This means 3 – 7 > 5 is false. The true inequality is 3 – 7 < 5. The corrected inequality states that 3 – 7 is less than 5
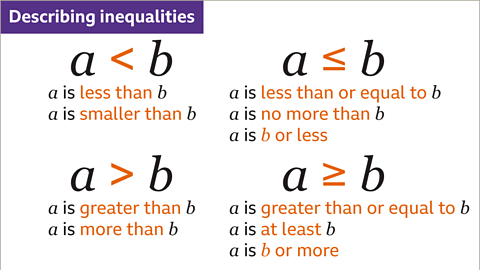
Image caption, The words used to describe an inequality can vary. For example, ‘𝒂 is greater than or equal to 𝒃’ can also be described as ‘𝒂 is at least 𝒃’.
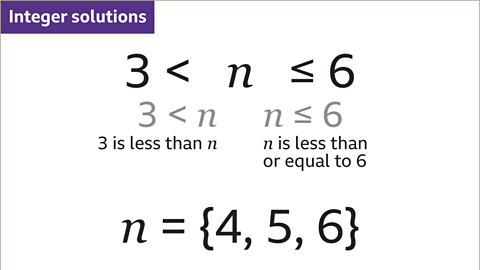
Image caption, When the variable is given between two inequalities and values, it may be possible to list the integer solutions. In this example, 𝒏 is the integer. 3 is less than 𝒏, which is less than or equal to 6. 𝒏 can be any integer that is greater than 3, up to and including 6. The set of integer solutions is {4, 5, 6}.
1 of 9
Question
Which inequality is used to state that 𝒏 is at least 8?
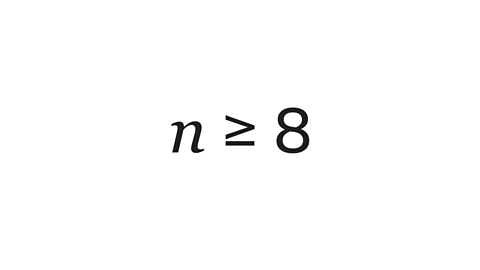
- Because 8 is the least the value can be, 𝒏 can be 8 or any greater value.
- 𝒏 is greater or equal to 8
- 𝒏 ≥ 8
Inequalities on a number line and listing integer solutions
Inequalities can be illustrated on a number lineA straight line on which numbers are marked at equal intervals..
- For a single inequality, with one value:
Draw a circle above the value on the number line.
- The circle is unshaded for < and >
- The circle is shaded for ≤ and ≥
Draw a horizontal line with an arrow in the same direction as the inequality:
- to the left with an arrow for < and ≤
- to the right with an arrow to the right for > and ≥
For a single inequality there are an infinite number of integer solutions. These can’t be listed in a solution set.
- For an inequality with two values:
Draw circles above the values on the number line.
- The circle is unshaded for < and >
- The circle is shaded for ≤ and ≥
Draw a horizontal line between the circles.
For an inequality with two values there are a finite number of integer solutions. This can be written as a solution set which is presented in curly brackets. For example, {2, 3, 4}.
Examples

Image caption, A number line can be used to illustrate an inequality.

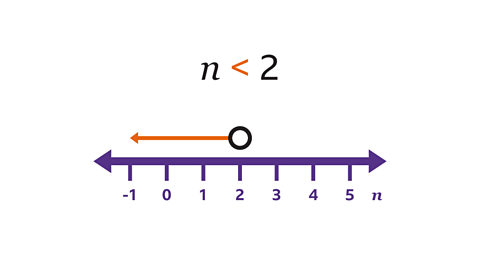
Image caption, Show the inequality 𝒏 < 2 on a number line.
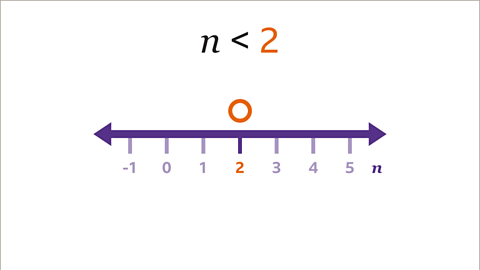
Image caption, The inequality uses the value 2. Draw a circle above the value 2 on the number line. The number line must show the value/s in the inequality and does not need to be a specific length. The circle is not shaded because 𝒏 is less than 2. 𝒏 cannot be 2
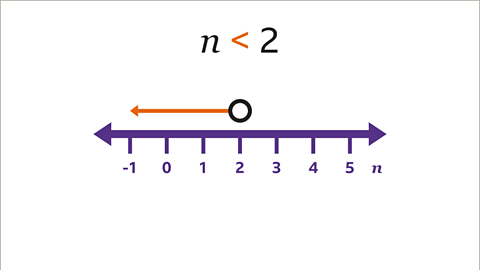
Image caption, To show that 𝒏 is less than 2, draw a horizontal line with an arrow pointing to the left (to lesser values). The arrowed line does not have to be a particular length, it just needs to show that 𝒏 can have values that are less than 2. The arrow points in the same direction as the inequality. The integer solutions for the inequality cannot be listed as a solution set because an infinite number of integers are possible.
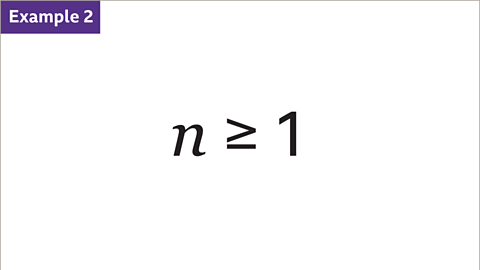
Image caption, Show the inequality 𝒏 ≥ 1 on a number line.
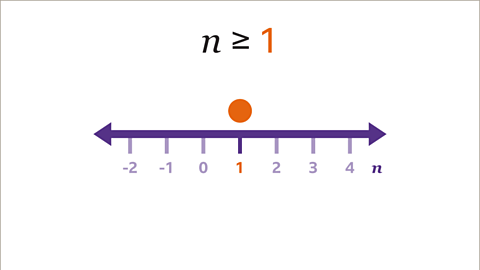
Image caption, The inequality uses the value 1. Draw a circle above the value 1 on the number line. The circle is shaded because 𝒏 can have the value 1
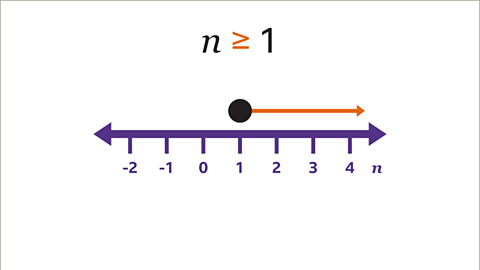
Image caption, To show that 𝒏 can be greater than 1, draw a horizontal line with an arrow pointing to the right (to greater values). The arrowed line does not have to be a particular length, it just needs to show that 𝒏 can have values that are more than 2. The arrow points in the same direction as the inequality. The integer solutions for the inequality cannot be listed as a solution set because an infinite number of integers are possible.
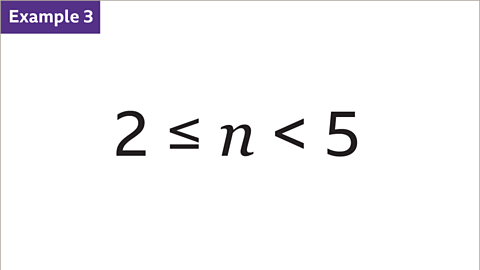
Image caption, Draw the inequality 2 ≤ 𝒏 < 5 on a number line.
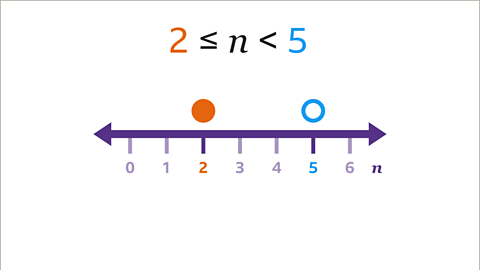
Image caption, The inequality uses the values 2 and 5. A shaded circle is above the value 2 on the number line, because 𝒏 can have the value 2. An unshaded circle is drawn above the value 5 on the number line, because 𝒏 cannot have the value 5
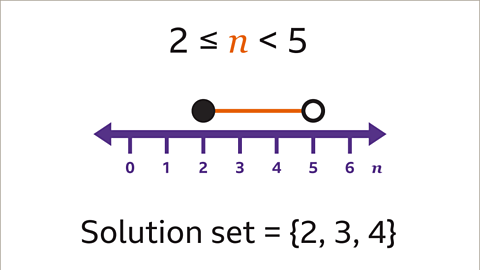
Image caption, Draw a horizontal line between the two circles to show that 𝒏 can take any value between the two numbers. The integer solutions for the inequality can be listed as a solution set because a finite number of integers are possible. In this example, 𝒏 can be 2 (solid circle), 3 or 4. 5 is not included, because the circle is unshaded. The solution set is {2, 3, 4}. The values of a solution set are listed within curly brackets.
1 of 10
Question
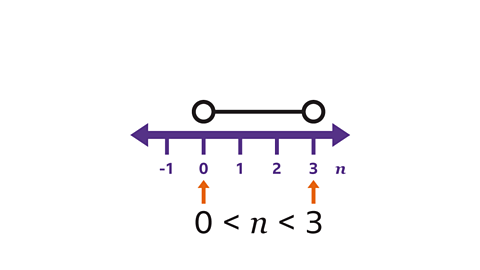
What inequality is shown on the number line?
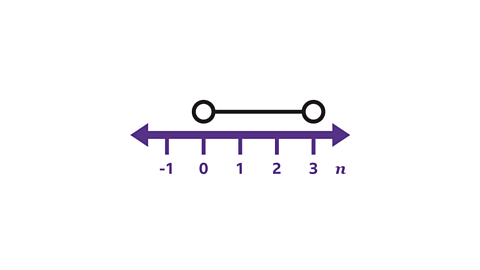
- The two values are 0 and 3
- The variable 𝒏 lies between these two values.
- The variable 𝒏 cannot have the value of 0 or 3, because the circles are not shaded.
- The inequality shown on the number line is 0 < 𝒏 < 3
Solving simple linear inequalities
A single inequality written with an expressionA mathematical sentence expressed either numerically or symbolically made up of one or more terms. may be solved by using inverse operationThe opposite of a mathematical process. Eg, the inverse of × 5 is ÷ 5. The inverse operation undoes the original process.:
Undo each process in the inequality by using the inverse operation. Inverse operations include addition and subtraction, and multiplication and division.
Start with the last operation and work back to the first.
For each step make sure that the inverse is applied to both sides of the inequality.
Once the variable is isolatedSet apart, alone. The variable is by itself on one side of the mathematical statement. write the solution as a simple inequality.
An expression between inequalities is solved using inverse operations in the same way:
- Apply each inverse operation to all three parts of the inequality.
- Write the solution as a variable between two inequalities.
Examples
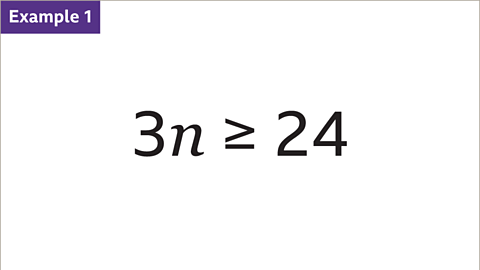
Image caption, Solve the inequality 3𝒏 ≥ 24
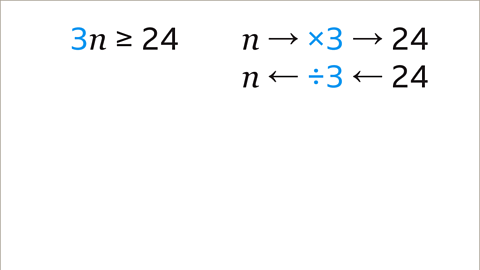
Image caption, The variable (𝒏) has been multiplied by 3 to give a value that is greater or equal to 24. The inverse of × 3 is ÷ 3
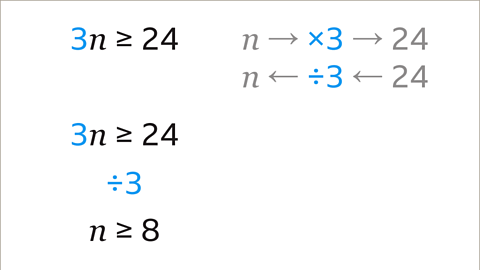
Image caption, Because the inverse of × 3 is ÷ 3, divide both sides of the inequality by 3. This gives 𝒏 ≥ 8. The 𝒏 is isolated. The solution to the inequality is 𝒏 is greater or equal to 8
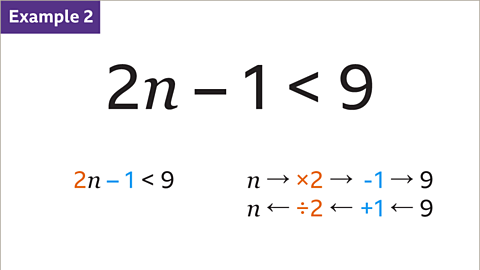
Image caption, Solve the inequality 2𝒏 – 1 < 9. The variable (𝒏) has been multiplied by 2. 1 is then subtracted to give a value that is less than 9. The inverse of × 2 is ÷ 2. The inverse of – 1 is + 1
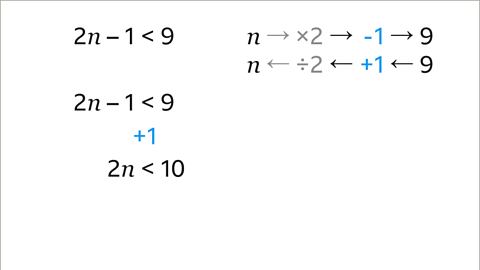
Image caption, The inverse of – 1 is + 1. Add 1 to both sides of the inequality. The inequality is now 2𝒏 < 10
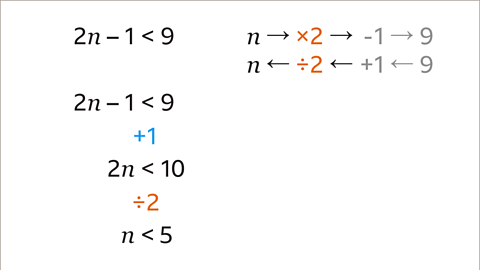
Image caption, The inverse of × 2 is ÷ 2. Divide both sides of the inequality by 2. The 𝒏 is isolated. The solution is n < 5
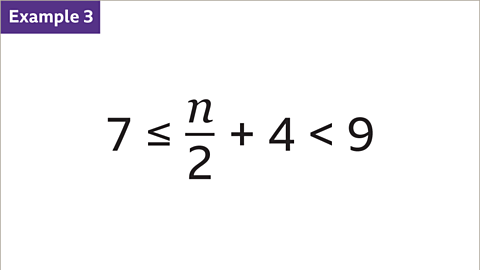
Image caption, 𝒏 is an integer. Find the integer solutions for 7 ≤ ⁿ⁄₂ + 4 < 9
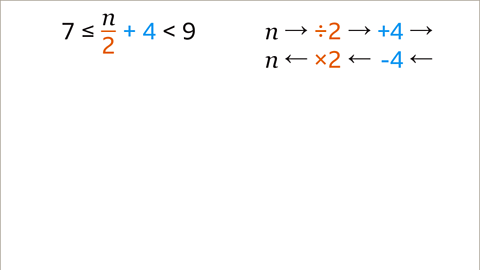
Image caption, The variable (𝒏) has been divided by 2. 4 is then added to give a value that is greater than or equal to 7 and is less than 9. The inverse of ÷ 2 is × 2. The inverse of + 4 is – 4
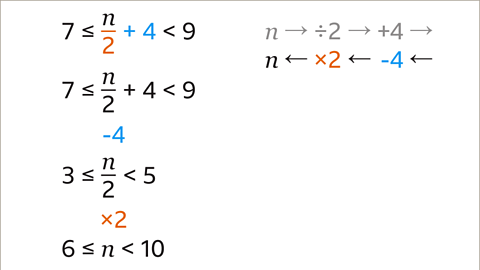
Image caption, The inverse of + 4 is – 4. Subtract 4 from each part of the inequality. The inverse of ÷ 2 is × 2. Multiply each part of the inequality by 2. The variable 𝒏 is now isolated. This makes the solution 6 ≤ 𝒏 < 10
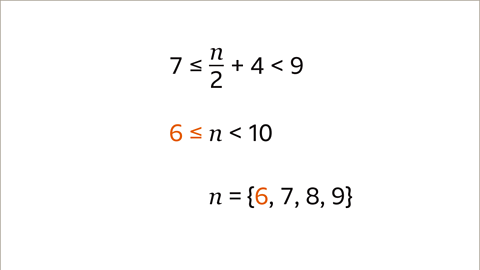
Image caption, The integer solutions for 6 ≤ 𝒏 < 10 are all the integer values that 𝒏 can be. The least value 𝒏 can be is 6, because 6 is less or equal to 𝒏. 𝒏 cannot be 10, because 𝒏 is less than 10. The integer values for 𝒏 can be 6, 7, 8 or 9. The solution set for 7 ≤ ⁿ⁄₂ + 4 < 9 is {6, 7, 8, 9}.
1 of 10
Question
Solve the inequality and list the integer solutions for 𝒏
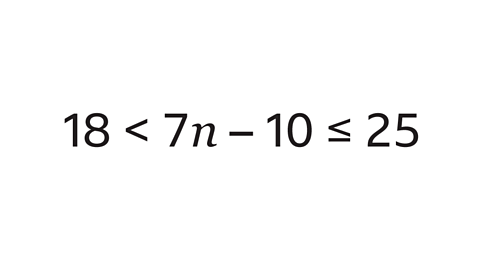
The variable (𝒏) has been multiplied by 7
10 is then subtracted to give a value that is greater than 18 and is less than or equal to 25
The inverse of × 7 is ÷ 7
The inverse of – 10 is + 10
10 is added to each part of the inequality.
Each part of the inequality is divided by 7
The solution is 4 < 𝒏 ≤ 5
The only integer solution for 𝒏 is 5. The solution set is {5}.
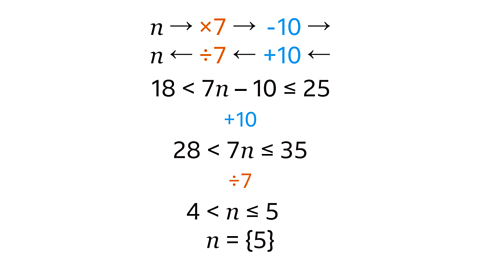
Practise using inequalities
Quiz
Game - Divided Islands
Play the Divided Islands game! gamePlay the Divided Islands game!
Using your maths skills, help to build bridges and bring light back to the islands in this free game from BBC Bitesize.
