Key points
- Characteristics like eye colour and genetic diseases are inheritanceThe passing of characteristics determined by genes from parents to offspring..
- A Punnett square can be used to work out the probability of offspring inheriting some characteristics.
- Heredity is the study of inheritance.
Video - gene inheritance
Cats come in many colours and patterns. These are determined by lots of different genes interacting. But some characteristics are inherited through just a single gene, including long or short hair in cats.
The different forms of a gene for a particular characteristic are called alleles, and they're represented using letters, for example in cats upper case H for short hair and lowercase h for long hair. Every organism inherits two alleles for each gene, one from each parent. The combination of alleles for a particular gene in an individual is called the genotype. And the way the genes are expressed, the appearance of the organism, is called the phenotype.
Some characteristics, like short hair in cats, are dominant. Just one dominant allele in the genotype determines the phenotype. In cats, long hair is recessive. So a cat only has long hair if it has 2 recessive long hair alleles.
When both of the alleles for a characteristic are the same, the individual is homozygous. When the two alleles are different, the individual is heterozygous. If two short haired cats breed, you might expect short haired offspring. But sometimes, long-haired kittens appear.
So how does this happen?
If a kitten has long hair, we know both of its alleles must be recessive. This also tells us that the parent cats are heterozygous. They are both short haired, so must have a dominant, short hair allele. But they must also both have a recessive allele to pass on to their long-haired kitten. The remaining kittens all have at least one allele for the dominant short hair. Some will be homozygous and some heterozygous, it's all down to chance!
We can work out the probability of particular genotypes or phenotypes arising using a simple model called a Punnett square – here we’re using two heterozygous short haired cats. First fill in the possible gametes from the parents, one along the top, and one down the side. Then work out all possible combinations of gametes to give you the potential genotypes of the offspring. This also gives you the possible phenotypes, kittens with a dominant allele will have short hair.
Now you can work out the probability of different genotypes occurring in the offspring. Here the probability is that 25% will be homozygous dominant, 50% heterozygous and 25% homozygous recessive. The expected phenotypes would be 75% short haired kittens and 25% long haired kittens.
However, the combination of gametes is completely random. We can predict the most likely result, but you could end up with any combination at all!
Can you answer these questions based on the video?
1. Which characteristic of cats is inherited by one pair of genes?
2. What are alleles?
Hair (or fur) length
Pairs of genes for one characteristic, one inherited from each parent.
Monohybrid inheritance
Monohybrid inheritance is the inheritance of characteristics controlled by one pair of geneA small section of DNA that gives a characteristic. only such as fur in animals and red-green colour blindness in humans. Very few characteristics are controlled by one pair of genes.
Scientists now think that the classic examples used in monohybrid inheritance may actually controlled by more than one gene. These include tongue rolling and ear lobe structure. You might learn about these examples as models to understand the process.
Alleles
The sperm and the ovum (egg cell) each carry half of the DNAThe store of genetic information for all living things, passed from parents to offspring. from the parent. These join together during fertilisationThe joining of male and female gametes (sperm and ova or eggs). to form a new organism, with approximately half of the DNA from each parent. So there are almost always two copies of each gene. Pairs of genes for a characteristic are called alleles. Therefore there are alleles for almost every one of your characteristics.
Predicting alleles in offspring
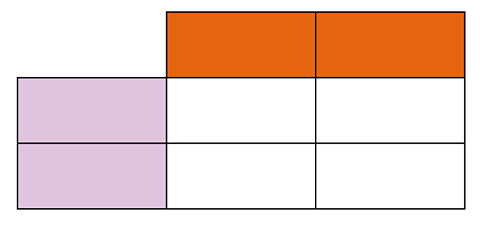
Monohybrid inheritance can be shown using Punnett squares. These show the probability of alleles in offspring.

The alleles for one parent go into the orange boxes along the top and the alleles for the other go into the purple boxes on the left. It doesn’t matter which way around the parents go. The four possible alleles for the offspring are shown in the white boxes.
For example, here are the three possible genotypeThe combination of alleles in an organism. Genotypes are often written as pairs of letters - one for each gene. and their phenotypeThe appearance of the organism’s genotype. Phenotypes are often written as words. for hair length in cats. Remember short hair is dominant geneJust one dominant gene in the genotype means that its appearance is seen in the phenotype.
| Genotype | Phenotype |
|---|---|
| HH (homozygous dominant) | Short hair |
| Hh (heterozygous) | Short hair - because H is dominant over h |
| hh (homozygous recessive) | Long hair |

Here is how to work out the probabilty percentage of genotype and phenotype of the offspring of two long-haired cats (hh).
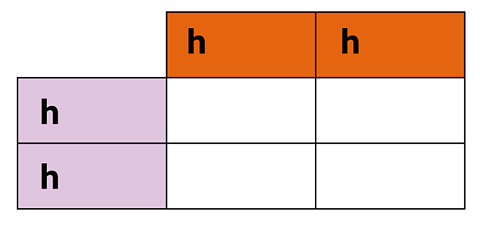
Step 1
Add the parent genotypes to the left and top boxes.

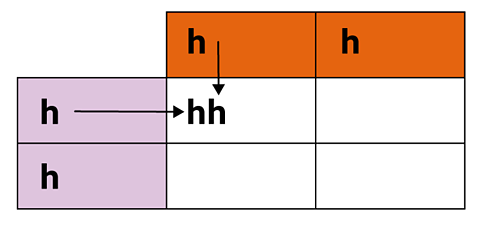
Step 2
Copy the letters from the orange and purple boxes as shown. This reveals the genotype of the offspring.

Step 3
Continue for the other white boxes until all four are filled.
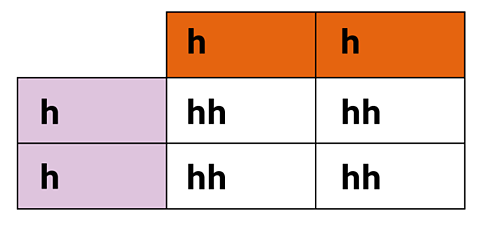
Step 4
Analyse the results. It is important to do this for all three genotypes and both phenotypes.
- HH – zero out of four so 0%
- Hh – zero out of four so 0%
- hh – four out of four so 100%
- Short hair – zero out of four so 0%
- Long hair – four out of four so 100%
It is important that the genotypes (HH, Hh, hh) always add up to 100% and so do the phenotypes (short and long hair).
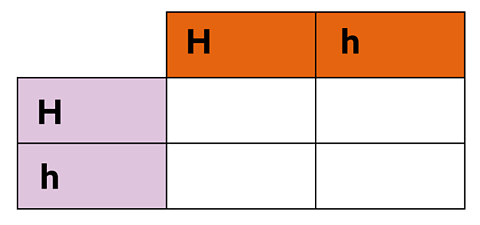
Repeat the process for two heterozygous short-haired cats.

Complete the table then analyse the results to see the percentages of genotypes and phenotypes.
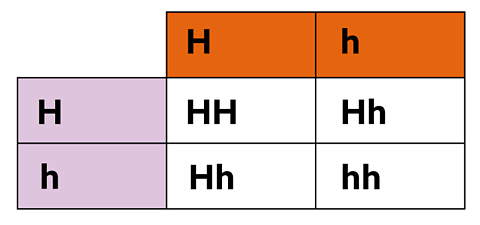
- HH – one from four so 25%
- Hh – two from four so 50%
- hh – one from four so 25%
- Short hair – three from four so 75%
- Long hair – one from four so 25%
Inheritance of genetic disorders
A genetic disorder is an inherited medical condition. It can be passed from parents to their children. Examples include cystic fibrosis, sickle cell disease and haemophilia.
Parents who are heterozygous for these conditions are called carriers. They do not usually have the disorder themselves. Two heterozygous parents (carriers) have a one in four chance of passing it to their children.
This is shown in this Punnett square for cystic fibrosis.
An individual who is homozygous (cc) with the recessive geneA recessive gene is only observed in the phenotype if no dominant gene is present. allele will develop cystic fibrosis.
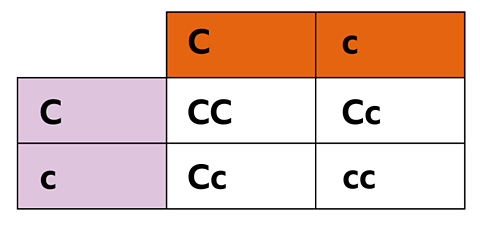
- CC – one from four so 25%
- Cc – two from four so 50%
- cc – one from four so 25%
- Without cystic fibrosis – three from four so 75%
- With cystic fibrosis – one from four so 25%
Quiz - Inheritance
GCSE exam dates 2025
Find out everything you need to know about the 2025 GCSE exams including dates, timetables and changes to exams to get your revision in shape.

More on Inheritance and genetics
Find out more by working through a topic
- count5 of 11

- count6 of 11

- count7 of 11
- count8 of 11
