Key points
- When working in a laboratory, follow the lab rules.
- Hazard symbols give information about chemicals and materials.
- When working in a lab, take safety precautions.
Why is lab safety important?
Accidents can easily happen. It’s best to minimise risk to avoid getting hurt.
Video
Watch the video below about safety rules in the lab.
Look out for the labels on the bottles of chemicals that the scientist has in the lab, as well as how they use the Bunsen burner
Presenter 2: We will be looking at safety in the laboratory. It is important to keep yourself and everyone around you safe and free from injury. Always follow the lab rules.That means understanding risk and potential hazards.
Presenter 1: A hazard is something that can cause harm.
Presenter 2: Such as burning yourself on a Bunsen burner or other equipment that gets very hot.
Presenter 1: Notice the symbol here on this chemical container. This is one of many important hazard symbols that can often appear on containers or equipment to tell us about the hazards. We should always be aware of the risks with chemicals.
Presenter 2: This sign means that the chemical is corrosive. These chemicals attack and destroy materials such as wood, metal and skin as soon as they come into contact with them.
Presenter 1: This sign means that the chemical is flammable. It could easily catch fire. The second thing we need to be aware of is risk.
Presenter 2: The risk is how likely a hazard will cause harm. See what can happen here.
Presenter 1: Another example is to never put broken glass in the waste paper bin. This is a very high risk because people could cut themselves when they empty it.
Presenter 2: Control measures are very important. They are precautions we can put in place either to reduce the risk or the severity of the hazard.
Presenter 1: Such as safety goggles, bags clear from floor and hair tied back. These are all examples of good practice.
Presenter 2: Now, let's assess the risk of this experiment – the evaporation of the water from a solution of salt. Here, you could leave the water to evaporate naturally over a week, or use a Bunsen burner in two minutes.
Presenter 1: Are the risks the same in these two setups?
Presenter 2: No. Risks are higher in the experiment using a Bunsen burner.
Presenter 1: Appropriate control measures to take will be wearing safety goggles, not touching the equipment until cool and stopping heating when the salt begins to spit.
Student 1: It's starting to bubble, which means it's heating up and hopefully eventually it'll start to evaporate.
Presenter 2: Remember, in case of accidents, firstly tell an adult.
Student 2: Miss, there's been an accident.
Teacher: Where is it, Mickey…?
Presenter 2: Accidents happen and as long as lab safety rules have been followed then nobody will get in trouble.
Presenter 1: By not telling an adult, other people could be put at risk from an accident.
Presenter 2: So, now we have looked at how to judge hazards and risks and use control measures to minimise them, in order to keep us all working safely.
Risk and hazard

A hazardSomething that can cause harm. is something that can cause harm. A riskThe chance that harm will be caused. is a chance that a hazard will cause anybody harm.
The type of harm that could be caused is often shown using a hazard symbol A label giving important information about dangers associated with a chemical or material.. Hazard symbols can also be seen on items in the home.

Hazard symbols

Image caption, Warnings about hazards are often seen in everyday life. If these warnings are ignored, accidents can happen. In the lab it is important to know what hazard symbols mean.

Image caption, If materials are hazardous then they are labelled with hazard symbols.
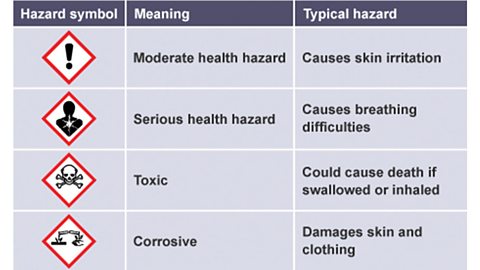
Image caption, These are some of the most common hazard symbols.

Image caption, Here are some more common hazard symbols that can be found in the lab.
1 of 4
On the bottle of hazardous chemical, there were three hazard symbols. Name one of them.
flammableSomething that catches fire easily. , moderate health hazard, or dangerous to the environment.
Spot the hazard symbols
What is the name for a label on a bottle that tells us a substance could cause harm?
A hazard symbol.
Lab rules
To reduce the risk of harm in the lab, it’s important to take precautionActions to take to reduce risk before doing something..These precautions are often given as a set of general lab rules to follow.Lab rules are put in place to keep everyone as safe as possible.These are some of the most important rules to follow.
Top 10 laboratory safety rules

Image caption, Do not enter the lab without permission
To keep everyone safe in the lab, a member of staff must be present. There could be dangerous equipment or chemicals left in the lab.

Image caption, Dress for practical work
Before starting practical work, long hair should be tied back and ties should be tucked in. These items can easily catch fire so make sure they can’t fall into a flame. Put safety goggles on before collecting any equipment and wear gloves to protect your hands if instructed to do so.

Image caption, Follow instructions from the person in charge
Guidance and instructions will make sure the experiment should work, helps to keep everyone safe, and reduces the risk of damaging equipment. If instructed to ‘stop’ during an experiment, then stop. This is because there may be a risk nearby.

Image caption, Make sure your working area is safe
This means bags and coats are safely out of the way; they can be trip or fire hazards. Stools should be tucked under benches. Always stand up during practical work if possible.

Image caption, Never run in the lab
Carefully walking around the lab helps to reduce the risk of trips, slips and banging into other people and equipment.

Image caption, Don’t eat or drink
Eating in the lab could be dangerous as spilt chemicals on the desk could get onto food and end up being accidently eaten. Drinking is dangerous as spillages can damage equipment, and bottles of chemicals can be mistaken for drinking containers.

Image caption, Do not taste or sniff chemicals
Some chemicals are harmful, poisonous or toxic. Even sniffing a chemical can be dangerous.

Image caption, Never leave an unattended Bunsen burner on a blue flame
A Bunsen burner would usually be on a blue flame during an experiment. When the Bunsen burner is not being used, it should either be on the yellow safety flame so that others can see it, or turned off.

Image caption, Check that electrical equipment is safe
Before starting to use electrical equipment, make sure it is in good condition. Look at the wires, check they aren't frayed or loose. Make sure all liquids are a safe distance from electrical equipment. Never put anything into an electrical plug socket, except for a safety plug, as it risks electrocution.

Image caption, Know what to do in case of accidents
Firstly, tell an adult. Accidents happen and as long as lab safety rules have been followed then nobody will get in trouble. By not telling an adult, other people could be put at risk from the accident. Never put broken glass in the waste paper bin.
1 of 10
Precautions
Plan for hazards and risks by thinking about what precautions to take in certain situations. Follow these steps:
- First identify the hazard.
- Then think about what could increase the risk.
- Finally, consider what precautions can be taken to reduce the risk.
Examples are shown in the table below.
| Hazard | Risks increased by… | Precaution to reduce risk |
|---|---|---|
| corrosiveA substance that breaks down metals and hurts body parts like skin and eyes. acid | Bottle of acid being close to edge of a bench. | Store acid away safely or at least move away from the edge of the bench. |
| Flame from a Bunsen burner | Having loose clothing or hair hanging down that could catch fire. | Tie hair back, tuck in ties and shirts. |
| Bags on the floor | People running, not seeing the bags and tripping up. | Store bags under benches safely out of the way and walk carefully around the room. |
| Fumes from chemicals | Lack of ventilation in the room so fumes could harm the nose and lungs. | Open windows to allow movement of air in and out. |
Lab safety
Using a Bunsen burner
The correct precautions must be taken when using a Bunsen burner, but first, it is important to know how to use it.
How to use a Bunsen burner:
- Make sure there are no breaks or holes in the gas hose.
- Follow lab rules: safety goggles, tie hair back, tuck in your tie.
- Put the Bunsen burner on a heat-resistant mat, making sure it isn’t near the edge of the bench.
- Turn the collar to ensure the air hole of the Bunsen burner is closed.
- Hold a lit splint 1-2 cm above the top of the barrel of the burner.
- Turn on the gas at the gas tap, and the Bunsen burner will burn with a yellow flame.
- Extinguish the splint and place it on the heat-resistant mat.
Bunsen burner

When you light the Bunsen burner, the flame will be yellow - this is often known as the ‘safety flame’ because you can see it.
The blue flame is used for heating. It is hotter because more air can flow through the Bunsen burner but it is harder to see.
Turning the collar of the Bunsen burner lets different amount of air in and changes the temperature of the flame.
A combustionBurning in oxygen. reaction takes place when the Bunsen burner is lit.

What colour is the flame when it is being used for heating?
Blue.
Test your knowledge
Quiz - Working safely in the lab
Did you know?

Hazard symbols are the same all over the world. Before 2017, symbols looked different in many countries, which wasn’t helpful for moving chemicals around the world.
Bunsen burners are named after the German scientist Robert Bunsen.

GCSE exam dates 2025
Find out everything you need to know about the 2025 GCSE exams including dates, timetables and changes to exams to get your revision in shape.

More on Working scientifically
Find out more by working through a topic
- count2 of 11

- count3 of 11

- count4 of 11

- count5 of 11
