Key points
- A diseaseAn illness affecting plants and animals. causes health problems by affecting an organism's body, organs, tissue or cells.
- There are many different types of disease that exist in the world today.
- Diseases can be caught, develop over time or be inherited.
Types of illness
Communicable diseases are those which are infectious. This means they can be transferred from one organism to another. An example of this is the common cold.
Non-communicable diseases are not infectious. This means they cannot be transferred between one organism and another. An example of this is chronic lung disease. geneticPassed on by genes or inherited by parents. diseases are also considered to be non-communicable. An example of this is sickle cell anaemia.
Non-communicable: Cancer
cancerA disease caused by normal cells changing so that they grow and divide in an uncontrolled way. The uncontrolled growth causes a lump called a tumour to form. is a non-infectious disease, therefore we say it is non-communicable. It is not caused by a pathogensBacteria, fungi and viruses that cause disease.. Some lifestyle factors are linked to cancer, such as eating a poor diet, being exposed to radiation and smoking. However, there are also cancers that do not have a specific known cause, and research is ongoing into what might cause them.
Cancer happens when the cells in a person's body grow out of control. This often leads to a tumour. Some tumours are benign, which means that they do not spread. Other tumours are malignant, which means that they spread to other parts of the body and cause other tumours to grow.
Treatments for cancer include surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy, which uses harsh drugs to try and kill the cancerous cells. There are also treatments that are still being trialled, such as immunotherapy.
How a malignant tumour spreads
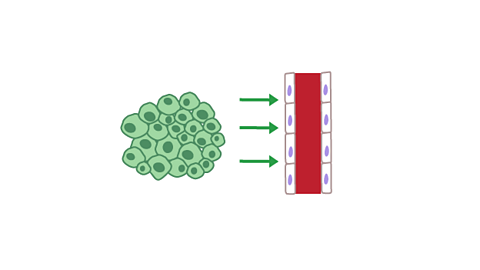
Image caption, A tumour secretes chemicals to nearby blood vessels
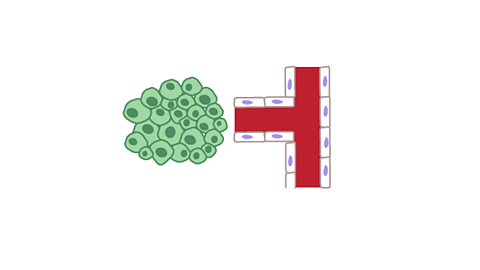
Image caption, The chemicals stimulate the blood vessels to grow, and they grow around the tumour
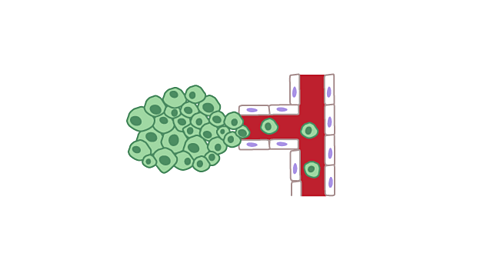
Image caption, Cancer cells detach from the tumour and are transported through the blood vessels
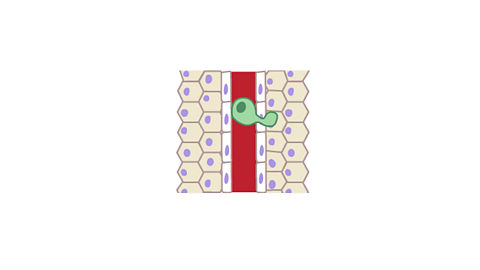
Image caption, A malignant cell squeezes through a blood capillary wall
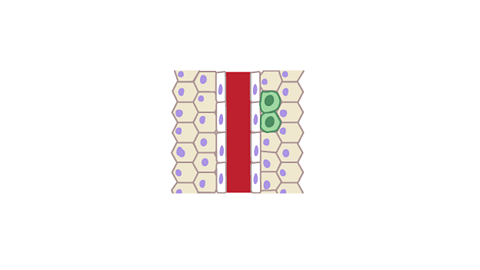
Image caption, The cancer cell divides outside the wall and a second tumour begins to grow
1 of 5
Communicable: Measles
Measles is a highly infectious viral illness that can sometimes lead to serious complications. It is therefore considered to be an example of a communicable disease.
Symptoms can include:
- cold-like symptoms, such as a runny nose, sneezing and a cough
- sore, red eyes
- a high temperature or fever
- small greyish-white spots on the inside of the cheeks
Measles can be unpleasant, but will usually pass in about seven to ten days without causing any further problems. However, in some cases measles can lead to serious and potentially life-threatening complications. These can include infections of the lungs and brain.

The measles virus is contained in the millions of tiny droplets that come out of the nose and mouth when an infected person coughs or sneezes. You can easily catch measles by breathing in these droplets or, if the droplets have settled on a surface, by touching the surface and then placing your hands near your nose or mouth. There is no specific treatment for measles. If you contract measles, you are advised to rest, take painkillers and drink plenty of fluids to help ease the symptoms until it has run its course. However, measles is now uncommon in the UK because of the effectiveness of vaccination.

Other diseases
| Communicable | Non-communicable | Non-communicable and genetic |
|---|---|---|
| Measles | Cancer | Cystic fibrosis |
| HIV | Type 2 diabetes | Alzheimer'sA disease that affects the brain, typically in elderly people, leading to confusion, memory loss, behaviour changes, and eventually difficulty speaking, walking and swallowing. |
| Gonorrhoea | Heart disease | Sickle cell anaemia |
| Malaria | Chronic kidney disease | Haemophilia |
Test your knowledge
Quiz
Write a short paragraph to answer each of the following questions. Tap 'Show answer' to see the points you could have included.
Name the two different types of cancerous tumours and four ways cancer might be treated.
The two types of cancerous tumours are:
- Benign tumours which do not spread
- Malignant tumours which spread around the body, causing more tumours to grow
Treatments for cancer include:
- Surgery
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy - a cancer treatment that involves using harsh drugs to try and kill cancerous cells
- Immunotherapy - a cancer treatment which is still being trialled
What are the usual symptoms of a person who has measles?
- Cough
- Runny nose
- Sore red eyes
- A high temperature
- Small greyish-white spots on the inside of the cheeks
GCSE exam dates 2025
Find out everything you need to know about the 2025 GCSE exams including dates, timetables and changes to exams to get your revision in shape.

More on Health and disease
Find out more by working through a topic
- count3 of 5
- count4 of 5
