What is wind energy?
Wind power is a renewable energy source which is used to generate electricity.
In this article you can learn about:
- Where wind comes from
- What happens inside a wind turbine
- What the advantages and disadvantages of wind energy are
This resource is suitable for energy and sustainability topics for primary school learners.
Video - What is wind energy?
Learn about wind energy and its advantages and disadvantages in this video.
Watch this short video to find out where wind energy comes from and how it can be used as an energy source
Here’s Wind power – a renewable energy who loves to keep fit! She's a lively one…
Oh. Alright, not always.
Sometimes, she just can’t get moving.
But as soon as the wind blows, it’s work out time!
Humans discovered wind power a looong time ago.
And we’ve got better and better at building wind machines.
But where does wind come from?
Well, what really gets wind power moving is the sun.
The sun heats up air in some places more than others.
When air is warmed it rises, and cold air rushes in to take its place.
This movement of hot and cold air is how wind is generated.
It's kind of like when you let go of a balloon and all the air rushes out… Whoops!
The modern turbine has blades that keep turning even if there's not that much wind.
That's because they're perfectly shaped to capture the wind's kinetic energy.
The blades spin a shaft, which is connected to a generator.
Inside the generator, copper coils turn through a magnetic field to convert kinetic energy into electricity.
Whitelee Wind Farm, just outside Glasgow, is the biggest onshore wind farm in the UK - with 215 turbines!
It can generate enough electricity for almost 350,000 homes.
One of the best things about wind power is that she's a clean form of energy, meaning she doesn't burn anything or put any carbon in the atmosphere.
Plus we'll never run out of wind.
She doesn't work everywhere though, only in open spaces – like at sea or on a hill.
And she does have a couple of wee problems.
One is that she can harm birds.
The other… I don’t really like to say it, but…
Well, some people think she spoils the view!
That’s one of the reasons most new wind farms are being built out at sea.
Ah the wind’s up again.
Actually, that's a bit too fast…
Making me dizzy! Could you…?
Urgh… I'd better go…
Where does wind come from?
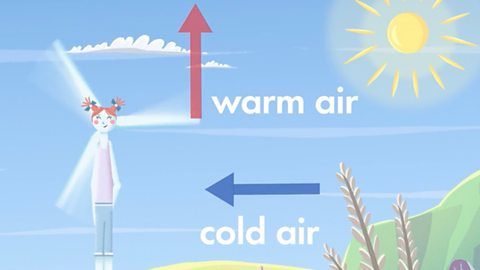
Wind is created when the Sun warms air in our atmosphere.
The air is heated more in places with more sun. When air is heated, it rises. Cold air rushes in to replace it, making wind.
This air is moving so it has kinetic energyEnergy that an object possesses because of its movement. A ball being thrown through the air has kinetic energy because it is moving. When water moves this is also an example of kinetic energy. .
Learn more about where wind comes from here: What is wind?

What is wind power?
Humans have been using the energy of the wind for thousands of years for example as sails for boats, as windmills to grind grain and make flour, and windpumps to pump water.
How do wind turbines work?
Wind turbines turn energy from the wind into electricity.
Turbines turn so that they face into the wind. The turbine blades are shaped so that even low winds will push them round. Kinetic energy from the moving air is transferred to the spinning blades.
The blades turn a shaft which is connected to a gearbox. Here the slow spin of this shaft is used to spin a much faster second shaft.
The second shaft is attached to a generator. Inside the generator are magnets which spin round very fast past coils of copper wire. The spinning magnets make electricity start to flow through the copper wire. Kinetic energy is changed to electrical energy which travels through cables to the National GridThe name given to the network of pylons and power lines that transport electricity to our homes, schools, offices and businesses..
Wind turbines work best in open places where no obstacles block the wind. They are often part of larger wind farms which are often high up on hills or out at sea.
Wind energy in Scotland
Onshore wind is Scotland’s main source of renewable energy. In 2020 about 70% of electricity generated in Scotland came from onshore wind.
Offshore wind is the third biggest source of electricity, after hydro. Windfarms like Beatrice Offshore Windfarm power hundreds of thousands of homes.
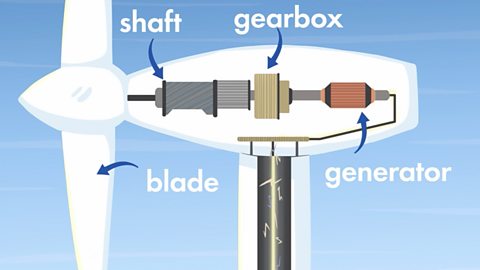
Image caption, Wind turns turbine blades, which spin a shaft. A gearbox uses this slowly spinning shaft to turn a second shaft that spins much faster. The second shaft connects to a generator and makes electricity. The electricity is sent through power lines to a substation, then on to homes, businesses and schools.

Image caption, The inside of a wind turbine generator, showing the ring of magnets surrounded by ring of copper wires. (Mike Hudson / Alamy Stock Photo)

Image caption, Whitelee Wind Farm on Eaglesham Moor, south of Glasgow, is the biggest onshore windfarm in the UK. With 215 turbines it can generate enough electricity for 350,000 homes. (Iain Masterton / Alamy Stock Photo)

Image caption, Offshore wind farms are usually out at sea where there is lots of wind that can be used to generate electricity. This is Robin Rigg Wind Turbine Farm in the Solway Firth, off the Galloway coast in the South of Scotland. (Geof Kirby / Alamy Stock Photo)

Image caption, Beatrice Offshore Windfarm Ltd. in the Moray Firth, off the Caithness coast in the North Sea. (SSE)
1 of 5
The advantages and disadvantages of wind power
Advantages of wind power
- Wind power is renewable and an unlimited resource – we will never run out of wind.
- Wind power creates no carbon emissions and is not harmful to the environment.
- Electricity from wind power is cheap once turbines are set up.
Learn more about how wind affects people and the environment: How does the wind affect daily life?
Disadvantages of wind power
- When there is no wind, windfarms do not generate any electricity.
- In some places wind farms can harm birds that nest in or fly through the area.
- Some people think wind farms spoil the view of the sea or countryside.

Key words about wind power
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. – Energy that an object possesses because of its movement. A ball being thrown through the air has kinetic energy because it is moving. The kinetic energy of the wind turns the blades on the wind turbine generating electricity.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. – A long pole. The shaft is part of the wind turbine that turns, helping to generate electricity. The energy in the wind turns the blades that are connected to the main shaft, which turns and spins a second shaft, which spins a generator to create electricity.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. – A machine that is used to make electricity. When the generator head is turned, this energy is converted to electrical energy.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. – A generator contains coils of copper wire. When a ring of magnets spins, electricity starts to flow through the wires.
Test your knowledge
Quiz
Challenge

Draw a diagram to describe:
- How wind is created from the Sun.
- How a wind turbine creates electricity.
What is wind? videoWhat is wind?
Find out what wind is and how we can measure it.

How does the wind affect daily life? videoHow does the wind affect daily life?
What are the advantages and disadvantages of wind?

Secrets of an Engineer. audioSecrets of an Engineer
Lorna Bennet is part of a team who build wind turbines.

More on Sustainability
Find out more by working through a topic
- count25 of 28

- count26 of 28

- count27 of 28

- count28 of 28
