Key points
The light that we see is made up of many different colours.
There are three primary colours: red, green and blue. They can be combined in different ways to make every other colour.
The colour of an object is determined by the wavelength of light that it reflects.
Video
A photographer explains the science of colour
What are light and colour?
White light from the Sun is a mixture of colours, each with a different frequency. You can use a prism to split (or disperse) white light into a spectrum of colours: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet. Dispersed means that the colours are separated out.
We see higher frequencies of light as blue or violet, lower frequencies of light are seen as red and orange. Green light is in the middle.
Professor Brian Cox explains how white light disperses into different colours
Eyes and colour
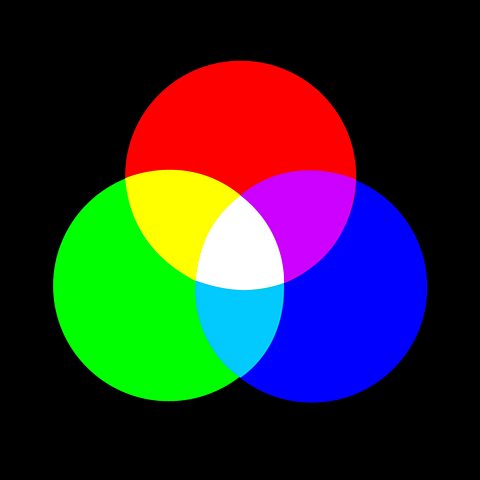
Our eyes only detect three colours: red, green and blue. By combining these, however, we can perceive many different colours.
By mixing red light and green light, for example, we can see yellow. If all three are mixed together we see white light.
Objects absorb and reflect light differently. A lemon reflects yellow light, all the other colours are absorbed and so are not seen by our eyes.

Who needs to know about light and colour?
Light and colour are fundamental for photography. An object can have different coloured lights shone on it to bring out certain features.
Colour quiz
GCSE exam dates 2025
Find out everything you need to know about the 2025 GCSE exams including dates, timetables and changes to exams to get your revision in shape.

More on Waves
Find out more by working through a topic
- count10 of 15

- count11 of 15

- count12 of 15

- count13 of 15
