Key points
- Evaporation occurs when a liquid slowly turns into a gas below its boiling point.
- Crystallisation is a separation technique used to obtain crystals of a solid solute.
- When a solution is heated, the solvent evaporates and crystals of the solute are left behind.
Game - creating copper sulfate crystals
Play an Atomic Labs experiment where you can produce copper sulfate crystals.
You can also play the full game
What would be left behind if a bowl of salty water was left out in the sun?
Salt crystals. The water would evaporate so the dissolved salt would end up left behind in the bowl.
Video
Watch this video to find out all about evaporationWhen a liquid turns into a gas at temperatures below its boiling point. and crystallisationA separation technique used to obtain large crystals of a solute from a solution. .
You wouldn’t know it, but this water contains about ten tablespoons of salt. The soluble salt has dissolved into the water to make a salty solution. Luckily, I know how to get my salt back, using a process called evaporation!
See, in this salt solution there are water molecules and salt particles all mixed together. The particles in a liquid are constantly jiggling around, and the warmer the liquid is, the faster they’ll move.
Sometimes, near the top of the glass, the water particles will be going fast enough to escape into the air.
This is evaporation, when a liquid changes state to become a gas.
As we've just seen, the rate of evaporation can be increased by heating the solution. So, if I left some of the salt solution on a sunny windowsill, the heat from the sun would warm up the water and slowly it would evaporate into the air.
But if I didn’t want to wait that long, I could speed up the evaporation even more by heating it.
I’ll put the salt solution in an evaporating basin, and use a heat source like a Bunsen burner to gently increase the temperature of the water.
The particles are really whizzing about in the water, and they’re escaping into the air, or evaporating, faster than ever.
Before long, the water level drops. Even after we take the heat away, the liquid continues to evaporate, leaving crystals of salt behind.
That’s because the particles of salt are bigger than the water particles and need more energy to evaporate. So when the water is all gone, they stick together in solid crystals. It’s called crystallisation.
But we still need to wait for the water over there to evaporate.
After a couple of days, the solution I left on the windowsill has also evaporated. The energy from the sun has warmed the solution, speeding up evaporation. Like before, the water has turned into gas in the air and the salt has been left behind.
But this salt looks different - the crystals are bigger. That’s because when crystallisation happens more slowly, the crystals can grow bigger.
Why did the salt crystals appear faster in the solution which was heated using the Bunsen burner?
Because the hotter a liquid is, the more energy the particles have, so the faster the liquid will evaporate.
What is evaporation?
Evaporation describes the process of a liquid turning into a gas. Evaporation is a slower process than boilingWhen a liquid turns into a gas as it absorbs energy from the surroundings. because it occurs at temperatures below the boiling pointThe temperature at which a pure substance boils from a liquid into a gas. For example, the boiling point of pure water is 100°C. The boiling point is also the temperature at which a gas will condense into a liquid. of the liquid.

Evaporation occurs at all temperatures, boiling happens at a fixed temperature depending on the liquid.


Did you know?
Puddles dry up because of evaporation. Puddles do not boil because the temperature on earth is always below 100°C - the boiling point of water.

How is evaporation involved in the water cycle?
Water evaporates from the seas, oceans, lakes and rivers. It condenses in clouds to form rain.
Using evaporation to separate a solution
Evaporation can be used as a technique to separate the solid soluteThe solid (or occasionally a gas) which dissolves into a solvent (liquid) in order to make a solution. For example, the main solute in sea water is sodium chloride. from the solventThe liquid in a solution which dissolves the solute. For example, the solvent in sea water is water. in a solutionA mixture made when a solute (usually a solid) dissolves into a solvent (a liquid). Sea water is a solution of salt dissolved into water.. The solvent is the liquid, and when the solution is heated, the solvent evaporates. The solute is left behind as crystals.
In a lab the heat is usually supplied by a Bunsen burner, and the solution is heated in an evaporating basin.
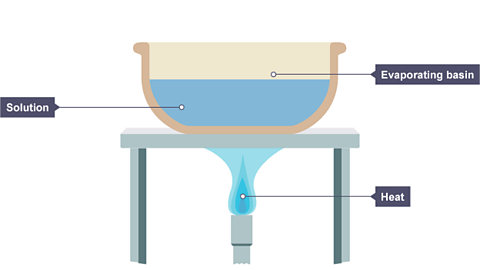
Image caption, A solution is placed in an evaporating basin and heated with a Bunsen burner.
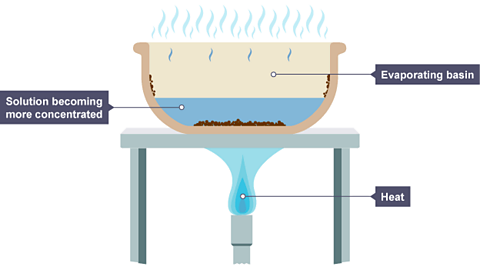
Image caption, The volume of the solution has decreased because some of the water has evaporated. Solid particles begin to form in the basin.
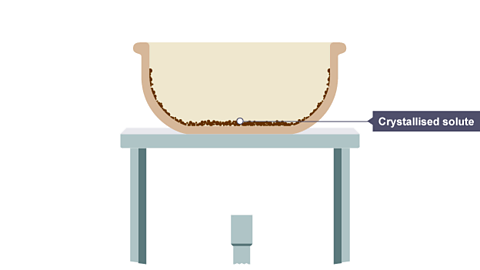
Image caption, All the water has evaporated, leaving solid crystals behind.
1 of 3
Describe and explain how evaporation can be used to obtain copper sulfate crystals from copper sulfate solution.
Copper sulfate solution is placed into an evaporating basin and heated using a Bunsen burner. The water (the solvent) heats up and evaporates. The copper sulfate (the solute) does not evaporate. The copper sulfate turns into dry crystals when all the water has evaporated.
Crystallisation

Crystallisation is similar to the evaporation technique used to separate a solid solute from a solution but is done over a longer period of time.
Crystallisation produces the largest possible crystals of the solute, because the slower the evaporation process, the larger the crystals.

Here are the steps for crystallisation:
- Rather than heating the evaporating basin directly with a Bunsen burner, it is often better to warm it gently and slowly over a beaker of boiling water.
- Heat the solution until half the solvent (water) has evaporated, which makes the solution more saturatedWhen a solution contains so much solute that no more will dissolve. .
- Leave the solution to cool and large crystals will form slowly.
- Put the evaporating basin in a warm place so the rest of the water evaporates.
What is the main difference between what is produced in crystallisation and evaporation?
Crystal size.
This is because crystallisation produces larger crystals than evaporation.
Test your knowledge
Quiz
Try the experiment online
Try out this experiment in Atomic Labs. Go to the Chemistry lab and try the creating copper sulfate crystals experiment.
Atomic Labs game. gameAtomic Labs game
Try out practical experiments in this KS3 science game

Teaching resources
Looking for more teaching resources? In this short video, students take practical experiments with water in the University of Cambridge’s Department of Chemistry with Dr Peter Wothers.
BBC Teach has thousands of free, curriculum-linked resources to help deliver lessons - all arranged by subject and age group.
GCSE exam dates 2025
Find out everything you need to know about the 2025 GCSE exams including dates, timetables and changes to exams to get your revision in shape.

More on Pure and impure substances
Find out more by working through a topic
- count2 of 7

- count3 of 7

- count4 of 7

- count5 of 7

