What are the key learning points about prescribed practical C7?
A carboxylic acid is an organic compound with a -COOH functional groupAn atom, or group of atoms, that determines the main chemical properties of an organic compound..
Carboxylic acids can carry out the same reactions as other acids, for example the reactions with metals and metal carbonate.
Carboxylic acids are weak acids, and will react more slowly than other, stronger acids like hydrochloric acid.
What are carboxylic acids?
Investigate the reactions of carboxylic acids
A carboxylic acid is an organic compound with a -COOH functional group.
Carboxylic acids can carry out the same reactions as other acids such as hydrochloric acids.
However, carboxylic acids are weak acids, so will react more slowly than other acids and have a less acidic pH value.
Remember:
All acids are soluble in water.
They release H+ ions in water.
They release hydrogen gas when reacted with a metal.
They release carbon dioxide gas when reacted with a metal carbonate.
They have pH values less than 7.
In this practical you will compare the reactions of a carboxylic acid (ethanoic acid) with the reactions of hydrochloric acid.
Reaction 1: How to test the pH of carboxylic acid
In this investigation you use universal indicator paperPaper stained with universal indicator, a chemical solution that produces many different colour changes corresponding to different pH levels. to compare the pHScale of acidity or alkalinity. A pH (power of hydrogen) value below 7 is acidic, a pH value above 7 is alkaline. Neutral solutions have a pH of 7. of ethanoic acid with hydrochloric acid.
Investigate the pH of carboxylic acids.
What apparatus and chemicals are used in reaction 1?

Test-tubes (x2)
Measuring cylinder (10 cm3)
Universal indicator or pH meter
Ethanoic acid 0.1 mol/dm3
Hydrochloric acid 0.1 mol/dm3
What are the steps involved in carrying out reaction 1?
Using a measuring cylinder, measure 5 cm3 of hydrochloric acid and add to a test-tube.
Repeat step 1 with ethanoic acid into a separate test-tube.
Add 5 drops of universal indicator to each test-tube and record the pH or use a pH meter to record the pH.
What observations can be made about this experiment?
Hydrochloric acid has a low pH value (1-2).
Ethanoic acid has a higher pH value (3-5).
This tells us that the hydrochloric acid released more H+ ionAn atom or molecule that has either a positive or negative electrical charge. than the ethanoic acid, even though they are both the same concentration.
We can say that ethanoic acid is a weaker acid than hydrochloric acid as it only partly ionises in water.
Hydrochloric acid is a strong acid and completely ionises in water.
Reaction 2: How to compare the reaction of magnesium with both acids
Comparison of the reaction of magnesium with hydrochloric and ethanoic acids.
Ethanoic acid and hydrochloric acid will both react with magnesium, though hydrochloric acid will react more vigorously.
The reactions that take place are:
magnesium + hydrochloric acid → magnesium chloride + hydrogen
magnesium + ethanoic acid → magnesium ethanoate + hydrogen
What apparatus and chemicals are used in reaction 2?
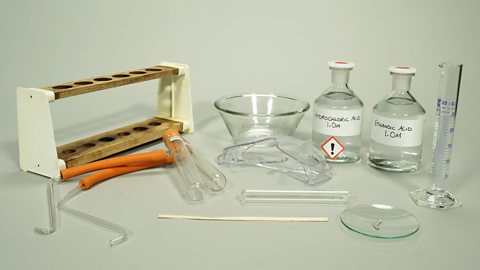
Boiling tubes
Delivery tube
Test tube
Basin
Boiling tube rack
Measuring cylinder (25 cm3) safety glasses, wooden splint
1 mol/dm3 hydrochloric acid
1 mol/dm3 ethanoic acid
2 x 1 cm strips of magnesium ribbon
What are the steps involved in carrying out reaction 2?
Fill the basin and test-tube with water, let the test tube rest on the bottom of the basin
Measure 20 cm3 of ethanoic acid using the measuring cylinder and add to the boiling tube
Repeat step 2 with hydrochloric acid, place both boiling tubes in the boiling tube rack
Add the magnesium strip to each boiling tube – ensuring that the Mg is fully immersed in the acid, allow the reaction to proceed for 10 seconds and record your observations.
The gas produced can be collected using the delivery tube and the test-tube in the basin of water.
Observations
For both hydrochloric acid and ethanoic acid the following is observed:
- Gas produced.
- Solid magnesium disappears.
- Colourless solution formed.
- Heat produced.
The reaction of magnesium takes place more quickly with hydrochloric acid, and more heat is released.
If the gas produced is tested, for both acids, it will cause a lit splint to burn with a squeaky pop, indicating the presence of hydrogen gas.
Reaction 3: How does ethanoic acid react with calcium carbonate?
Reaction of ethanoic acid with calcium carbonate.
Ethanoic acid and hydrochloric acid will both react with calcium carbonate, though hydrochloric acid will react more vigorously.
The reactions that take place are:
calcium carbonate + hydrochloric acid → calcium chloride + water + carbon dioxide
calcium carbonate + ethanoic acid → calcium ethanoate + water + carbon dioxide
What apparatus and chemicals are used in reaction 3?

Measuring cylinder (25 cm3)
Boiling tube
Test-tube
Disposable pipette/dropper
Test-tube rack
Ethanoic acid 0.5 mol/dm3
Calcium carbonate (3 g)
Universal indicator
Limewater (5 cm3)
What are the steps involved in carrying out reaction 3?
Using a measuring cylinder, measuring 15 cm3 of ethanoic acid and place into the boiling tube
Add 5 drops of universal indicator to the acid
Using a clean measuring cylinder, measure 5 cm3 of limewater and place into a test-tube. Place the test-tube and boiling tube side by side in a test-tube rack.
Carefully add the calcium carbonate to the acid – record your observations, especially any colour changes to the indicator.
Using the disposable pipette/dropper, collect the gas produced by opening and closing the dropper above the reaction in the boiling tube.
Once the gas has been collected in the disposable pipette/dropper, bubble the gas through the limewater and record your observations.
Observations
For both hydrochloric acid and ethanoic acid the following is observed:
Gas produced
Solid calcium carbonate disappears
Colourless solution formed
Limewater turns cloudy when the gas is bubbled through it.
The reaction of calcium carbonate takes place more quickly with hydrochloric acid than ethanoic acid.
How much do you know about prescribed practical C7?
More on Unit 3: Prescribed practicals
Find out more by working through a topic
- count8 of 9

- count9 of 9

- count2 of 9
