What are the key terms?
Alleles: Different forms of a gene (eg dominant or recessive)
Dominant allele: Always expressed when present (eg T)
Recessive allele: Only expressed when no dominant allele is present (eg tt)
Genotype: The combination of alleles an organism has (eg TT, Tt or tt)

Phenotype: The outward expression of a gene - the physical appearance (eg tall or short)
Homozygous: Both alleles are the same (eg AA or aa)
Heterozygous: The two alleles are different (eg Aa)
Punnett squares: A grid used to determine genotype frequencies
What is a monohybrid cross?
A monohybrid cross involves one characteristic controlled by a single gene with two alleles.
During meiosisCell division that produces haploid gametes., gametes (sex cells) receive only one allele for each gene as they have half the number of chromosomes, so parents pass on one allele for each characteristic to their offspring.
Crossing purebred tall (homozygous dominant – TT) and short parent plants (homozygous recessive – tt) results in the first generation (F1) offspring all being tall (heterozygous – Tt).
Large numbers of offspring are needed to provide an accurate ratio because fertilisation is random, and Punnett squares only show the chance of possible offspring.
Who was Gregor Mendel?
Gregor Mendel, a monk known as the "Father of Genetics," made significant contributions to our understanding of inheritance.
He grew pea plants and observed that their characteristics varied.
By crossing (mating) plants with different traits and analysing their offspring, he drew important conclusions about inheritance, despite not knowing about chromosomes or genes.
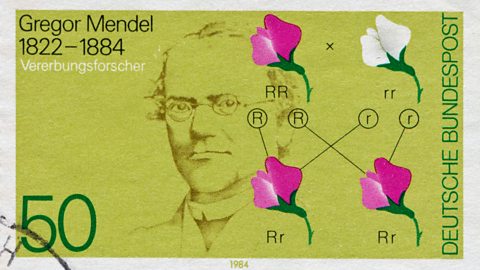
Mendel concluded:
Characteristics are determined by factors within the organism (now known as genes).
These factors can exist in two different forms (now known as alleles).
The two factors (alleles) in an individual separate during gamete formation (now known as meiosis).
What is the genotype for the tall plant?
Is it TT or Tt?
If a farmer only wants to grow tall plants to sell, how does she ensure that there are no small plants?
She only breeds the plants with the TT genotype.
How does she know which plant has the TT genoptype?
Carry out a test (back) cross.
Test (back) cross
The genotypes TT and Tt both produce a tall phenotype. In order to establish the genotype, a test cross is used.
The organism in question is crossed with a homozygous recessive individual (tt).
If no short plants (tt) are produced in the offspring the unknown parent was homozygous (TT).
If any short plants (tt) are present in the offspring the unknown parent was heterozygous (Tt).
Pedigree diagrams
Pedigree diagrams are used to show how a genetic condition is inherited in a family.
They are often used to advise individuals within a particular family if they are carriers of a condition.
Test your knowledge
Watch: Inheritance
More on Genetics
Find out more by working through a topic
- count4 of 6

- count5 of 6

- count6 of 6

- count1 of 6
