How is sex determined in humans?
In humans, sex is determined by the sex chromosonesThe structure made of DNA that codes for all the characteristics of an organism..
Females have two X chromosomes (XX).
Males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY).
meiosisReduction division in a cell in which the chromosome number is halved from diploid to haploid. forms haploidReduction division in a cell in which the chromosome number is halved from diploid to haploid. gametes (sperm and egg cells).
All eggs contain one X chromosome.
Half of sperm contain one X chromosome and half contain one Y chromosome.
A mother always passes on an X chromosome, while a father can pass either an X or a Y.
During fertilisationThe joining of male and female gametes (sperm and ova or eggs)., there is a 50% chance that a sperm with an X chromosome will fuse with the egg, resulting in a girl (XX), and a 50% chance that a sperm with a Y chromosome will fuse, resulting in a boy (XY).
What are some genetic conditions?
Some genetic conditions are inherited, meaning they are passed from parent to child.
They are caused by mutations, which are random changes in the DNA or the number of chromosonesThe structure made of DNA that codes for all the characteristics of an organism..
Currently, there are no cures for genetics conditions.
Haemophilia
Haemophilia is a blood disorder where people cannot clotA clump of platelets and blood cells that forms when a blood vessel is damaged. their blood, leading to excessive bleeding.
It is caused by a recessiveAn allele that will only show in the phenotype if there is no dominant allele present (i.e. when two recessive alleles are present). allele on the X chromosome, so it is sex-linked.
Sufferers are almost exclusively males because they only have one X chromosome and need just one recessive allele to show the condition.
Only in very rare cases a female will have two recessive alleles and be a sufferer.
Females with one normal and one recessive allele are carrierSomeone who does not suffer from a condition but carries the allele and can pass it to his or her offspring.. They do not have Haemophilia symptoms but can pass the recessive allele to half of their children and pass the condition to their sons.
| Genotype | Phenotype |
|---|---|
| XHY | Normal male |
| XhY | Haemophiliac male |
| XHXH | Normal female |
| XHXh | Carrier female |
| XhXh | Haemophiliac female (very rare) |
Alleles:
- H = normal
- h = haemophilia
Cystic fibrosis
Mainly affects the lungs and digestive system, which become clogged with mucusA sticky substance produced by specialised cells in the body to trap dirt and microbes. leading to frequent infections.
It is caused by a recessive allele, which means only homozygousWhen the two alleles are the same (e.g. BB) recessive individuals (ff) will be affected.
| Genotype | Phenotype |
|---|---|
| FF | Normal |
| Ff | Carrier |
| ff | Sufferer |
Alleles:
- F = normal
- f = cystic fibrosis
Huntington's disease
Affects nerve cells in the brain, leading to brain damage.
It is caused by a dominant allele.
It usually becomes apparent after 40 years old by which time the person may have passed the allele onto their children
| Genotype | Phenotype |
|---|---|
| hh | Normal |
| Hh | Carrier |
| HH | Sufferer |
Alleles:
- h = normal
- H = Huntington’s
Down's syndrome
Individuals with Down's syndrome have reduced muscle tone and learning difficulties.
It is caused by an extra chromosome at chromosome 21.
This is not inherited and happens by chance during the formation of egg cells, giving them an extra chromosome (24 total). When fertilised by a sperm cell with 23 chromosomes, this results in a total of 47 chromosomes instead of 46.
Watch: An overview of genetic conditions
Genetic screening
Genetic screening involves testing people or groups of people for the presence of a particular allele or other genetic abnormality.
Pregnant mothers are offered a blood test at 10–14 weeks to assess the risk of having a child with Down's syndrome.
High-risk cases may then be offered amniocentesis, which is more accurate but carries a 1% risk of miscarriage, unlike the safer blood test.
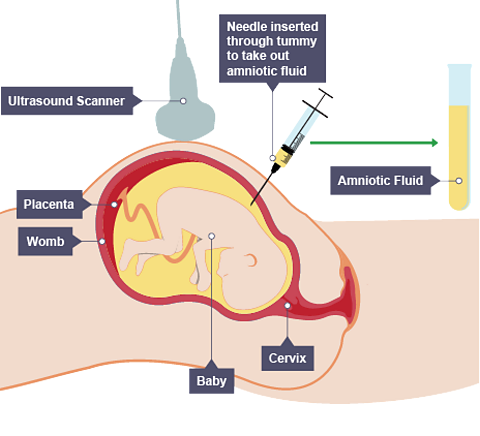
Amniocentesis procedure:
A needle is inserted into the amniotic fluidThe fluid surrounding a foetus that cushions it. that surrounds the foetusAn unborn baby. Usually eight weeks after conception. and fluid is withdrawn.
Chromosomes in foetal cells from the fluid are examined for genetic abnormalities such as Down's syndrome and cystic fibrosis.
Mothers at greater risk include:
Those with a family history of genetic conditions.
Those who previously carried a foetus with a genetic abnormality.
Older mothers.
Those with possible problems identified in earlier tests, such as blood tests.

What are some of the ethical issues from genetic screening?
Parents can be faced with difficult decisions if genetic screening shows their foetus has a genetic condition.
Ethical issues are questions about right, wrong and fairness, especially when decisions affect others' rights, privacy, or well-being.
Ethical questions:
Who decides who will be tested?
People should have the choice to be tested
Decisions for unborn babies are made by parents, is this right?
What are the benefits and risks of amniocentesis and blood tests?
Amniocentesis: more accurate but involves a small risk of miscarriage.
Blood Tests: safer but less accurate, often needing further testing.
What is the dilemma for carriers of genetic conditions?
Parents face emotional challenges and difficult decisions if genetic screening shows their foetus has a genetic condition.
It will allow them to access support.
Parents may be offered an abortion:
prevents suffering, poor quality of life, and ease the burden on parents and siblings.
the unborn child has a right to life and cannot voice their choice
Abortion is against some religious teachings
Should genetic information be available to wider society?
Pros: It could advance medical research.
Cons: Insurers or employers might misuse it, causing discrimination.
Solution: Strong laws are needed to protect privacy.
Quiz time!
More on Genetics
Find out more by working through a topic
- count5 of 6

- count6 of 6

- count1 of 6

- count2 of 6