Cell division
All cells have a cell cycle, where they grow, copy their DNA, and spilt into new cells during cell division.
There are two types of cell division – mitosis and meiosis.
What is the role of mitosis?
Mitosis produces two new cells (daughter cells) that are genetically identical (clones) to the parent cell and each other.
Mitosis allows organisms to:
grow
replace worn out cells and
repair damaged tissue
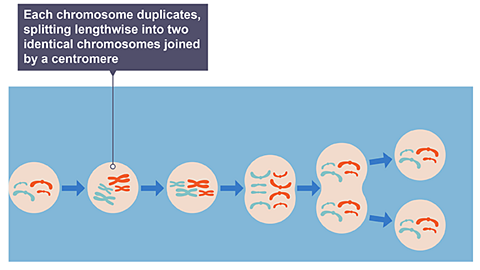
Image caption, Mitosis
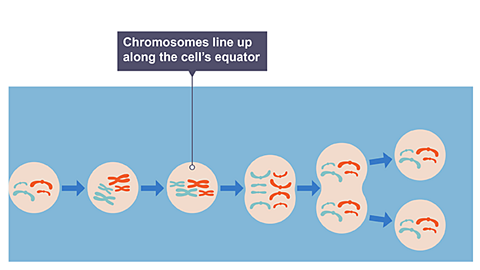
Image caption, Mitosis
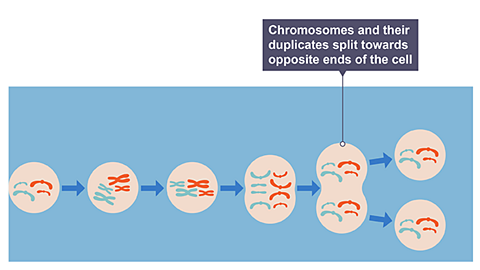
Image caption, Mitosis
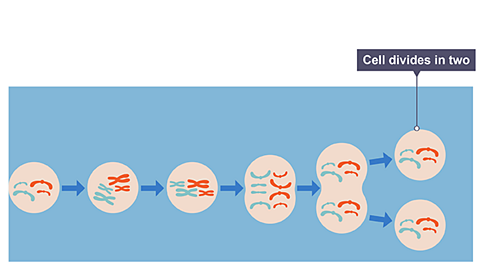
Image caption, Mitosis
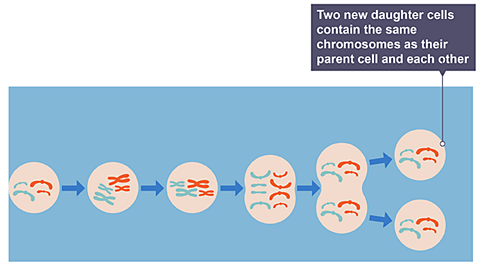
Image caption, Mitosis
1 of 5
What is meiosis?
Meiosis only produces gametes (sex cells) so occurs in the testesThe plural form of testis, the male organ that produces sperm. and ovariesA pair of organs in the female reproductive system where ova (eggs) and hormones are produced.. All sex cells contain half the number of chromosomes.
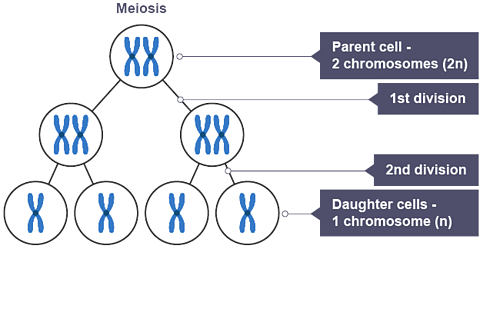
During meiosis, a diploid (2n) cell undergoes two divisions to reduce its chromosome number, resulting in four haploid (n) gametes with half the number of chromosomes.
Humans have 23 chromosomes in their sex cells.
The four gametes produced in meiosis are genetically different.
The process of independent assortmentA process that takes place during meiosis, in which chromosomes are reassorted. leads to all gametes being different.
Independent assortment and the random nature of fertilisation lead to variation in living organisms – no two organisms are the same (apart from identical twins).
During fertilisation the haploid nucleus of a sperm cell and the haploid nucleus of an egg cell fuse together to form a diploid zygote.
Test your knowledge
More on Genetics
Find out more by working through a topic
- count3 of 6

- count4 of 6

- count5 of 6

- count6 of 6
