Key points
- Heredity is the study of inheritance.
- Genetic conditions are inherited from parents.
What is a genetic condition?
A genetic condition is a condition or disease that is passed from one or both parents to their children. Unlike such as the common cold, genetic conditions cannot be caught by others. This makes genetic conditions non-communicable diseases.
It is important to remember that other non-communicable diseases like lung cancer are not genetic conditions, but often develop as a result of lifestyle choices like smoking. People who don't have genetic conditions but could pass them to their children are called carriers.
For relatives of people with genetic conditions, genetic testing can help them understand the chances of having children with these conditions.
Examples
Cystic fibrosis
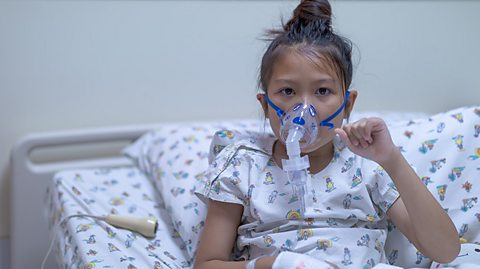
Cystic fibrosis causes the build-up of sticky mucus in the gas exchange systemThe lungs and airways - including trachea, bronchi and bronchioles - that exchange oxygen in air for carbon dioxide. and the digestive system. This causes infections in the lungs and makes it difficult to digest food.
Newborn babies are tested for cystic fibrosis and other genetic conditions shortly after birth. The symptoms of cystic fibrosis usually start in early childhood. Treatments help remove the mucus and reduce infection, but there is currently no cure. People with cystic fibrosis have a shorter than average life expectancy.

Sickle-cell disorder
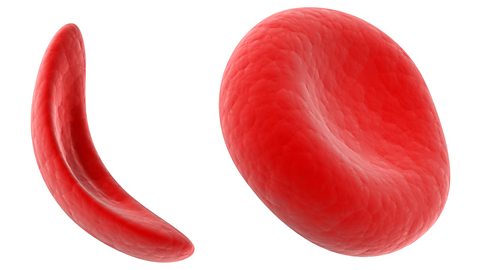
Sickle-cell disorder results in red blood cells with a sickle or crescent shape, rather than the characteristic bi-concaveA flat, disk shape with a dip on both sides to increase surface area. Red blood cells are this shape. shape. These cells do not live as long as normal cells, can carry less oxygen to the body's organs and can cause blockages in blood vessels. If these blockages are in the brain or heart, this can cause a stroke or heart attack.
Sickle-cell disorder is more common in people with African or Caribbean backgrounds. The symptoms usually start in early childhood. Treatments help manage the symptoms. The only cure is a bone marrowThe spongy material inside your large bones like those in your legs and hips, in which other cells are made. transplant, but this is a risky medical procedure. People with sickle-cell disorder have a shorter than average life expectancy.

Haemophilia
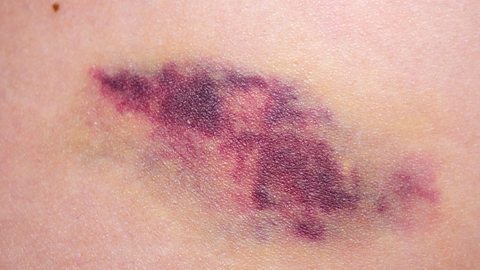
Haemophilia stops the blood clotting. People with haemophilia may have nosebleeds and bruises that last for a long time and have cuts that heal slowly.
People are usually diagnosed with haemophilia in childhood. There is no cure for haemophilia, but effective treatments are available, including injections that help blood clotting. People with haemophilia are advised to avoid contact sports and reduce the likelihood of cuts and bruises.

Inheritance key terms
| Key term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Heredity | The study of inheritance. |
| Inheritance | The passing of characteristics determined by genes from parents to offspring. |
| Gene | A short section of DNAThe store of genetic information for all living things, passed from parents to offspring., which is the genetic code for a characteristic. |
| Genotype | The combination of alleles in an organism - genotypes are often written as pairs of letters, one for each gene. |
| Phenotype | The appearance of the organism's genotype - phenotypes are often written as words, not letters. |
| Dominant gene | Just one dominant gene in the genotype means that its appearance is seen in the phenotype. |
| Recessive gene | A recessive gene is only observed in the phenotype if no dominant gene is present. |
| Heterozygous | A genotype with one dominant and one recessive gene. |
| Homozygous dominant | A genotype with two dominant genes. |
| Homozygous recessive | A genotype with two recessive genes. |
Test your knowledge
Quiz
Test questions
Write a short paragraph to answer the following question. Tap 'Show answer' to see five points you could have included.
Describe the symptoms of cystic fibrosis and how they are treated.
- Cystic fibrosis causes the build-up of sticky mucus in the gas exchange system and the digestive system.
- This causes infections in the lungs and makes it difficult to digest food.
- People with cystic fibrosis have a shorter than average life expectancy.
- The symptoms of cystic fibrosis usually start in early childhood.
- Treatments help remove the mucus and reduce infection, but there is currently no cure.
Write a short paragraph to answer the following question. Tap 'Show answer' to see seven points you could have included.
Describe the symptoms of sickle cell disorder and how they are treated.
- Sickle cell disorder results in red blood cells with a crescent or sickle shape, rather than the characteristic bi-concave shape.
- These cells do not live as long as bi-concave cells, can carry less oxygen to the body's organs, and can cause blockages in blood vessels.
- If these blockages are in the brain or the heart, this can cause a stroke or a heart attack.
- People with sickle cell disorder have a shorter than average life expectancy.
- The symptoms usually start in childhood.
- Treatments can help manage the symptoms.
- The only cure is a bone marrow transplant, but this is a risky medical procedure.
GCSE exam dates 2025
Find out everything you need to know about the 2025 GCSE exams including dates, timetables and changes to exams to get your revision in shape.

More on Inheritance and genetics
Find out more by working through a topic
- count10 of 11

- count11 of 11

- count1 of 11

- count2 of 11
