Key points
- The position of an element on the periodic table provides information about its properties.
- The majority of elements are metals and they are found on the left and in the middle of the periodic table.
- Most metals share a lot of properties, such as being good conductors of heat and electricity.
- Non-metals often have the opposite properties. For example, they are usually poor conductors of heat and electricity.
True or false?
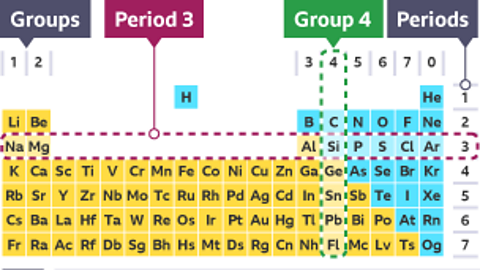
Calcium is a metal.
It’s true - calcium (Ca) is a metal!
We often hear about calcium being in milk and dairy products, but that is when the calcium atoms are chemically bonded to other atoms to form compounds.
Calcium is found on the left of the periodic table, surrounded by other metals. Calcium has the usual properties of a metal. For example it is a good conductor of heat and electricity.
Video
Watch this video to find out more about metalA substance which has the typical properties of a metal. Metals are found to the left and in the middle of the periodic table..
While you're watching, try to remember as many properties of metals as you can.
Gethin: Today, we've got super science teacher Miss Armit with us. What she doesn't know about chemistry is not worth knowing. And today, we're going to be looking at the periodic table.
Miss Armit - explain.
Miss Armit: So what we're going to look at today are the metal elements in Group 1 of the periodic table, along with the metal elements in the transition metal block of the periodic table and their properties.
Gethin: I think this is going to be good, isn't it.
So we're going to talk about transition metals, which are found in the middle of the periodic table. What are their key properties?
Miss Armit: So their key properties are they conduct electricity, they conduct heat, they are malleable - which means they're bendy - and they're shiny.
Gethin: All right. And what metals are we talking about here and what are they used for.
Miss Armit: Well, we've got copper and it's a really good conductor of electricity, so we use that in our wires. We've also got iron and aluminium and they're great at conducting heat, so we use these metals for our pots and pans. And gold and silver are used in jewellery, because they're shiny, they're malleable and unreactive with oxygen, so they don't rust easily.
Can you name a liquid transition metal?
Gethin: I would say mercury.
Miss Armit: Very good.
Gethin: Yeah.
Miss Armit: It's the only liquid transistor metal and because of its properties it's perfect for a thermometer. Why do you think that is?
Gethin: Well, it's something to do with the heat.
Miss Armit: Yeah, because mercury's a great conductor of heat. So, when it gets hot the space between the particles expands and then this rises up the thermometer.
Gethin: So, it's great for thermometers, but not so good for pots and pans.
Miss Armit: Exactly.
Gethin: They would just melt and it would just make a mess anyway.
Name as many properties of metals you can remember from the video.
The properties of metals listed within the video were:
- Conduct electricity
- Conduct heat
- Malleable
- Shiny
Metals and non-metals
Most elements in the periodic tableA table which lists all of the chemical elements and arranges them in a way that is useful. It allows us to spot patterns and make predictions about other elements. are metals, while non-metalA substance that has the typical properties of a non-metal. Non-metal elements are on the right hand side of the periodic table. account for around 20% of known elementA pure substance which is made from only one type of atom. Elements are listed on the periodic table..
The periodic table can be used to find out if an element is a metal or a non-metal. Metals are found on the left and in the middle, whereas non-metals are all on the right. It is possible to use information about an element’s physical propertyA property of an element or compound which can be directly observed or measured. For example, melting point, electrical conductivity, appearance at room temperature. to classifyTo arrange something into classes according to characteristics. In chemistry this is done according to physical and chemical properties. an element.
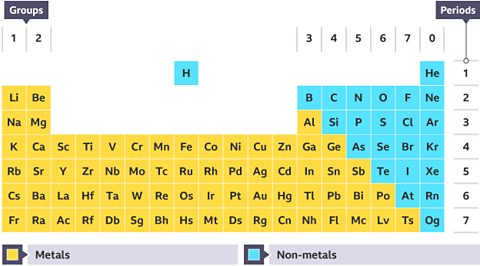
What type of elements make up around 20% of the periodic table?
Non-metals.
What are the properties of metals?
People use lots of metallic elements in their everyday lives. These include elements like iron, copper, gold and silver.
Most metals share similar properties with each other. For example:
- They have high melting pointThe temperature at which a pure substance melts from a solid into a liquid. For example, the melting point of pure water is 0°C. The melting point is also the temperature at which a liquid will freeze to a solid. and boiling pointThe temperature at which a pure substance boils from a liquid into a gas. For example, the boiling point of pure water is 100°C. The boiling point is also the temperature at which a gas will condense into a liquid. meaning they are solid at room temperature
- They are good conductorA material which allows heat or electricity to move easily through it. of heat and electricity
- They are shiny in their appearance
- They are malleableCapable of being hammered or pressed into a new shape without breaking.

Other common properties of metals are:
- They are hard and strong
- Have a high densityA measure of how heavy something is compared to its size. Measured in units of mass per unit of volume (e.g. g/cm3).
- They are sonorousAble to make a ringing sound when hit.


Did you know?
Copper has been used since ancient times in the manufacture of coins. This is because copper is malleable and can be hammered into shape.

Video - Metals
Metal elements don't need to have every single property of metals to be classified as a metal.
Watch this video to find out how some metals are different and don't always share the same properties.
Do all metals share the same properties?
No. There are some exceptions.
For example, there are differences in properties between the group 1 metals and the transition metals, and mercury (Hg) is a metal which is a liquid at room temperature.


What are the properties of non-metals?
Oxygen, carbon, sulfur and chlorine are examples of non-metal elements.
Non-metals have properties in common with each other. For example, they are often:
- Poor conductors of heat and electricity
- Dull in their appearance
- Weak and brittleSomething which is brittle is easily broken or shattered.
Some other common properties of non-metals are:
- Generally low melting and boiling points, meaning they are gases and liquids at room temperature
- Not sonorous

Some non-metals do not have all of these common properties.
For example, carbon has two main forms - graphite found in pencils, and diamond. Both graphite and diamond have very high melting points and are shiny.
Graphite conducts electricity, which is not typical of non-metals. However graphite is also brittle which is a typical property of non-metals.


An element doesn’t have to have every property of metals for you to classify it as a metal! As long as it has most metal properties, you can be confident that it is a metal.
Likewise, if an element has most of the properties of a typical non-metal, it would be sensible to suggest that it is non-metal.
Working scientifically
Data and observations help us to classify an element as a metal or a non-metal. We should use as many pieces of information as possible should be used to conclude.
Take the quiz below to see if you can correctly classify a range of elements.
Quiz

We must use as many properties as possible to distinguish if an element is a metal, or non-metal.
Find out more about how to conclude and evaluate in this learning guide.
Teaching resources
Looking for more resources for your chemistry lessons? In this short video, scientist Mark Miodownik visits the earliest known copper mines in Israel's Timna Valley to explain the discovery of the first metal - copper.
BBC Teach has thousands of free, curriculum-linked resources to help deliver lessons - all arranged by subject and age group.
GCSE exam dates 2025
Find out everything you need to know about the 2025 GCSE exams including dates, timetables and changes to exams to get your revision in shape.

More on Periodic table
Find out more by working through a topic
- count6 of 6

- count1 of 6

- count2 of 6

- count3 of 6