Key points
- Filtration is used to separate an insolubleA solid is insoluble if it does not dissolve in a specific solvent. For example, wax is insoluble in water. solid from a pure liquid or a solutionA mixture made when a solute (usually a solid) dissolves into a solvent (a liquid). Sea water is a solution of salt dissolved into water..
- Filtration usually involves a circle of filter paperA type of paper which allows pure liquids and solutions to pass through, but prevents particles of insoluble solid from passing through. folded to make a cone and placed into a filter funnel.
- The filtrate is the liquid which passes through the filter paper and the residue is the solid left on the filter paper.
Game - separating salt and sand
Play an Atomic Labs experiment exploring how to separate salt and sand.
You can also play the full game
A sieve can be used to separate small stones from fine sand. Why does sand pass through a sieve but stones do not?
Sand passes through a sieve because the sand particles are small enough to go through the holes in the sieve. The stones are too large to fit through.
Video
Watch this video about dissolveThe process when a solute is mixed with a solvent and the solute breaks into much smaller particles and spreads out. and solutions. It explains how filtrationA technique used to separate an insoluble solid from a pure liquid or a solution. is used to separate a mixture.
VOICEOVER: Solutions and filtration.
Solutions are a mixture in which a solid or a gas has completely dissolved in a liquid. We called the solid a solute and the liquid a solvent. A solid that will not dissolve in a specific liquid is described as insoluble.
For example, sand is insoluble in water. We can separate insoluble solids from a solution using filtration. Filter paper has thousands of tiny holes that allow the liquid molecules to pass through.
The filtered liquid is called the filtrate. The larger solid particles, in this case, the sand grains are unable to pass through and are left on the paper. And we call this the residue.
Ben: So, in front of me is a container of water and some children's play pit sand.
Dr. Tim: Right, Ben. If you take that sand and pour it into the water.
Ben: OK.
Dr. Tim: And give it a good shake there, get it all mixed up.
Ben: OK, it's in there. I'll put the lid on. Make sure it clicks, so I'm not gonna spill it. OK, you ready?
Dr. Tim: Ready. Right, now look at the result.
Ben: OK, here we go. I'll take the lid off. OK, there we go. Take a look at that. Now it's not a clear solution, is it? So, would we define the sand as insoluble in water?
Dr. Tim: That's exactly right, Ben. A substance is classed as insoluble if it does not fully dissolved in a specific solvent - in this case it's the sand is insoluble in water. Now, why don't you try and filter out that sand from the water.
Ben: OK, some filtration. Sure thing. So I'm going to pour this carefully. I'm just going to try and get the sand.
Dr. Tim: Right. Now, filtration is the process by which you remove an insoluble solid from the liquid. How's that going, Ben?
Ben: It's getting there. Just a little bit more, I think. OK, should we take a look?
Now, here we go. I don't know if you can see, but the container now contains style slightly clearer water at the bottom. And left in the filter paper here at the top, if I show you, is loads of the sand. Look at that, most of the grains are there and it's filtered through to the bottom.
Dr. Tim: Fantastic. And in doing that filtration, you've highlighted two new terms that have their own chemistry definitions.So, the solids that are too large to pass through the filter paper they're known as the residue.
Ben: OK. And the water in here is called?
Dr. Tim: That's called the filtrate. And the filtrate is slightly clearer than before, though, it is still a little bit cloudy. And that's because some of the smaller pieces of sand have managed to pass through the filter paper into the water.
Ben: I tell you what Dr.Tim, you weren't lying when you said there were a lot of definitions. But, I reckon they've all dissolved into my brain. Having filtered out all of the unnecessary residue in there.
Dr. Tim: Fantastic.
Ben: Thank you so much.
Why did the water molecules pass through the tiny holes in the filter paper, but the sand particles did not?
The water molecules are so small that they pass through the tiny holes in the filter paper. The sand particles are much larger, so they cannot fit through.
When is filtration used?
If a substance does not dissolve in a solvent, it is called insoluble. For example, sand does not dissolve in water, meaning it is insoluble.
Filtration is the process of separating solids from liquids using filter paperA type of paper which allows pure liquids and solutions to pass through, but prevents particles of insoluble solid from passing through..
The process can be used to separate an insoluble solid, for example stone or sand grains from a liquid. The liquid could be a pure liquid, for example water, or it could be a solutionA mixture made when a solute (usually a solid) dissolves into a solvent (a liquid). Sea water is a solution of salt dissolved into water., for example, salty water.
When a mixture of sand and water is filtered:
- the sand stays behind in the filter paper, it becomes the residueThe solid which has not passed through the filter paper during filtration..
- the water passes through the filter paper, it becomes the filtrateThe liquid which has passed through the filter paper during filtration..
The slideshow below demonstrates how filtration works.
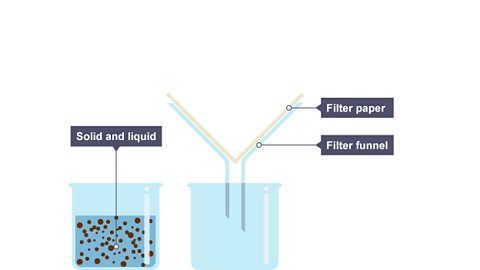
Image caption, One beaker contains a mixture of solid and liquid, the other contains a funnel with filter paper.
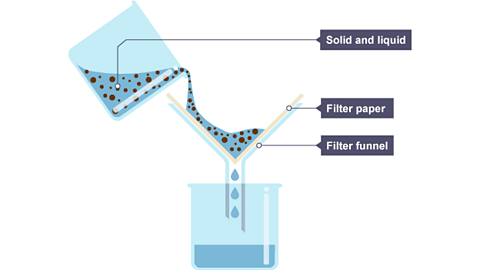
Image caption, The solid and liquid mixture is poured into the filter funnel.
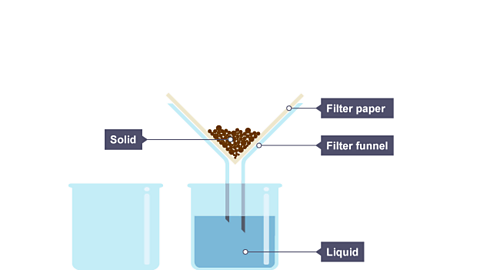
Image caption, The liquid drips through the filter paper but the solid particles are caught in the filter paper.
1 of 3
How does filtration work?

- The filter paper has lots of tiny holes in it, which are far too small to see.
- The particleA single piece of matter from an element or a compound, which is too small to be seen. Particles can be atoms, molecules or ions. of the liquid including any dissolved soluteThe solid (or occasionally a gas) which dissolves into a solvent (liquid) in order to make a solution. For example, the main solute in sea water is sodium chloride. will pass through the holes in the filter paper.
- If the liquid contains an insolubleA solid is insoluble if it does not dissolve in a specific solvent. For example, wax is insoluble in water. solid made of large particles, these larger particles cannot pass through the holes in the filter paper.

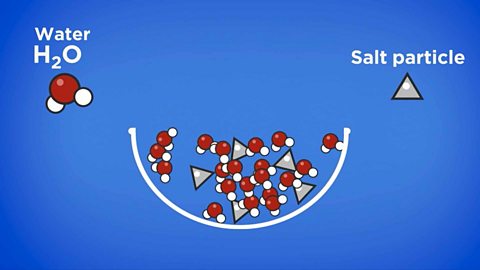
Why can’t filtration be used to separate salt from sea water?
Salt dissolves in water, so the solution of salt water passes through the filter paper. The particles of salt in the sea water are small enough to pass through the holes in the filter paper.
Working scientifically
Drawing scientific apparatus
There are photos and graphics of apparatus on this page including:
- Filter paper
- Conical flask
- Funnel
You could practise drawing scientific diagrams of the apparatus you can see in the photographs.

Keep your diagram simple and draw a 2-dimensional ‘cut-through’ style of diagram. To help, use a sharp pencil and a ruler for your straight lines, and don’t forget to include labels to make your diagram clear.
Find out more about drawing scientific apparatus.
Test your knowledge
GCSE exam dates 2025
Find out everything you need to know about the 2025 GCSE exams including dates, timetables and changes to exams to get your revision in shape.

More on Pure and impure substances
Find out more by working through a topic
- count1 of 7
- count2 of 7

- count3 of 7

- count4 of 7

