Key points about equations of a line and calculating gradient

- The general equation of a straight line is 𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 + 𝑐.
- 𝑚 is the gradientA measure of the slope of a line. and is the change in 𝑦-coordinates ÷ the change in 𝑥-coordinates.
- 𝑐 is the 𝑦-interceptThe point at which the line crosses the 𝑦-axis. and shows where the line crosses the 𝑦-axis.
Revise plotting straight line graphs to make sure you are confident with the link between equations and coordinates.
Video – Finding the gradient
Watch this video to find out how to determine if a straight line graph has a positive or negative gradient and how to calculate the gradient of a line.
Finding the gradient.
Any straight line graph has a constant gradient, which is calculated by the change in 𝑦 divided by the change in 𝑥, along any section of the graph.
The gradient is measuring the steepness of the graph, so a constant gradient means the steepness stays the same across the entire graph.
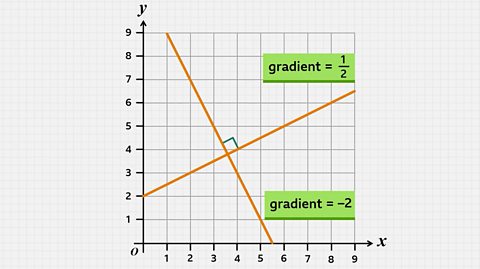
Before calculating the gradient, consider if it will be positive or negative.
To do this, imagine walking along the line from left to right. You would be going uphill, which means the gradient is positive.
Then choose any two coordinates on the line, for example (2, 3) and (8, 6), and then work out the change in 𝑦 divided by the change in 𝑥.
So, the gradient is one half.
Now, what if we draw another line?
Again, consider if the gradient will be positive or negative. This time, if you are walking along the line from left to right, you would be walking downhill, so the gradient will be negative.
Then, choosing two random points on the line and using the same method as before, we can work out that the gradient is –2.
Check your understanding
Equation of a line from a graph
The general equation of a straight line is 𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 + 𝑐.
𝑚 is the gradient of the line. 𝑚 is the coefficientA number or symbol multiplied with a variable or an unknown quantity in an algebraic term. For example, 4 is the coefficient of 4n². of 𝑥.
- The gradient shows how much the line goes up or down (vertical change) for every 1 unit it goes across (horizontal change).
- Gradient is calculated as
change in 𝑦 ÷ change in 𝑥. - A gradient of 8 is steeper than a gradient of 3.
- A negative value of 𝑚 shows the line has a downward slope.
- A gradient of –8 is steeper than a gradient of –3.
𝑐 is the 𝑦-intercept of the line. The 𝑦-intercept shows where the line crosses the 𝑦-axis.

Remember:
If the equation does not have 𝑦 as the subjectThe subject of a formula or equation is the variable on its own on one side of the equals sign, eg 𝑦 is the subject in 𝑦 = 3𝑥 + 5., the equation needs to be rearrangeTo rearrange an equation means to perform the same operation to the expressions on both sides of the equals sign. before finding the values of 𝑚 and 𝑐.
Follow the working out below
Check your understanding
GCSE exam-style questions
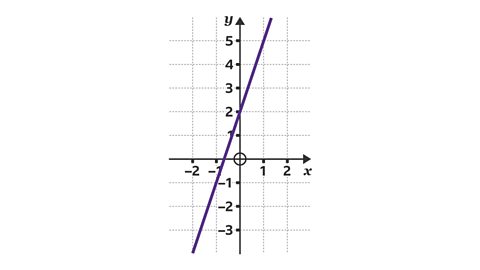
- The equation of a straight line is 𝑦 = 7 – 2𝑥.
What is the gradient and 𝑦-intercept of the line?
The gradient is –2. The 𝑦-intercept is 7.
- The gradient of the line is the number before the 𝑥, known as the coefficient of 𝑥.
- The gradient is –2.
- The 𝑦-intercept of the line is the number term on its own. The 𝑦-intercept is 7.
- What is the equation of the line?
𝑦 = 3𝑥 + 2.
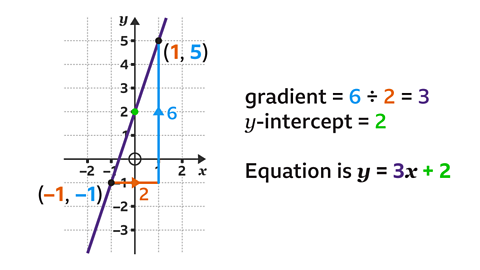
- The equation of a straight line is 𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 + 𝑐, where 𝑚 is the gradient and 𝑐 is the 𝑦-intercept.
- Draw a triangle to show the horizontal and vertical change.
- The change in 𝑦 divided by ÷ the change in 𝑥 always gives the gradient as 3.
- The line crosses the 𝑦-axis at 2, so the 𝑦-intercept is 2.
- What is the equation of the line?
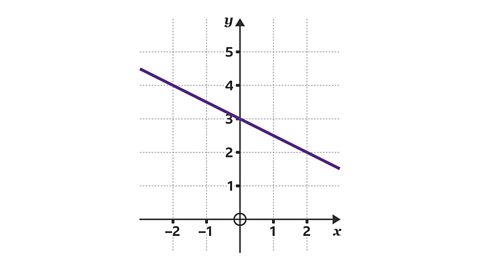
𝑦 =– \(\frac{1}{2}\)𝑥 + 3.
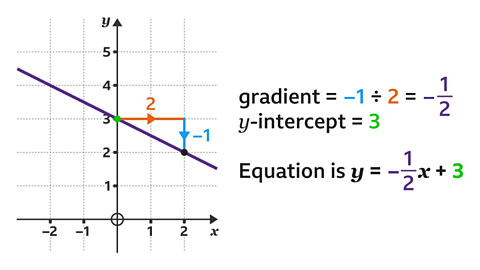
The equation of a straight line is 𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 + 𝑐, where 𝑚 is the gradient and 𝑐 is the 𝑦-intercept.
Draw a triangle to show the horizontal and vertical change. The line slopes downwards, so the gradient is negative.
The change in 𝑦 divided by ÷ the change in 𝑥 always gives the gradient as \(\frac{-1}{2}\).
The line crosses the 𝑦-axis at 3, so the 𝑦-intercept is 3.
Equation of a line from a graph – interactive activity
Working with the general equation of a straight line, 𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 + 𝑐, use the interactive activity to see what a graph looks like when plotted.
Select values for 𝑚, the gradient, and 𝑐, the intercept, to create a straight line.
Equation of a line between two points
The equation of a line is 𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 + 𝑐 where 𝑚 is the gradientA measure of the slope of a line. and 𝑐 is the 𝑦-interceptThe point at which the line crosses the 𝑦-axis..
To find the equation of a line from two points, follow these steps:
- Find the gradient by calculating change in 𝑦-coordinates ÷ change in 𝑥-coordinates.
- substituteIn algebra, to replace a letter with a number. the gradient for 𝑚 in the equation 𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 + 𝑐.
- Substitute the 𝑥 and 𝑦-coordinate of one of the points into the equation.
- solveTo solve an equation is to find the value of an unknown letter. the equation to find the value of 𝑐.
- Write the final equation using the found gradient and 𝑦-intercept.
GCSE exam-style questions

- Find the equation of the line that has a gradient of 3 and goes through the point (2, 5).
𝑦 = 3𝑥 + 1.
- Substitute the gradient of 3 in place of 𝑚 in the equation 𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 + 𝑐 to give 𝑦 = 3𝑥 + 𝑐.
- Substitute the values of 𝑥 and 𝑦 from the coordinates of the point (2, 5) to give 5 = 3 × 2 + 𝑐.
This means 5 = 6 + 𝑐. - Solve to find the value of 𝑐. Subtract 6 from each side. This gives the 𝑦-intercept as 𝑐 = –1.
- Write the equation of the line in the form 𝑦 = m𝑥 + c.
- Find the equation of the line that goes through the points (0, 3) and (2, 6).
𝑦 = 1∙5𝑥 + 3.
- Find the change in 𝑦-coordinates by subtracting the first 𝑦-coordinate from the second 𝑦-coordinate.
6 – 3 = 3. - Find the change in 𝑥-coordinates by subtracting the first 𝑥-coordinate from the second 𝑥-coordinate.
2 – 0 = 2. - Calculate the change in 𝑦 values ÷ the change in 𝑥 values. 3 ÷ 2 = 1∙5, so the gradient is 1∙5, or \(\frac{3}{2}\).
- The 𝑦-intercept is given by the point (0, 3), as this is where the line crosses the 𝑦-axis. The 𝑦-intercept is 3.
- Write the equation of the line in the form 𝑦 = m𝑥 + 𝑐.
- Find the gradient of the line between the points (– 6, 2) and (3, 5).
The gradient is \(\frac{1}{3}\).
- Find the change in 𝑦-coordinates by subtracting the first 𝑦-coordinate from the second 𝑦-coordinate.
5 – 2 = 3. - Find the change in 𝑥-coordinates by subtracting the first 𝑥-coordinate from the second 𝑥-coordinate.
3 – – 6 = 3 + 6 = 9. - The gradient is the change in 𝑦 values ÷ the change in 𝑥 values. 3 ÷ 9 = \(\frac{3}{9}\), which simplifies to \(\frac{1}{3}\).
Quiz – Equations of a line and calculating gradient
Practise what you have learned about equations of a line and calculating gradient with this quiz.
Now that you have revised how to work out equations of a line and calculate gradient, why not look at equations of parallel and perpendicular lines?
More on Algebra
Find out more by working through a topic
- count14 of 14
- count2 of 14

- count3 of 14